1,6-Heptadiene-3,5-dione, 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-, (E,E)-, Curcumin, Curcumin Phytosome, Diferuloylmethane, Mervia, Phytosome, Curcumin, Turmeric Yellow, Yellow, Turmeric



| Name | Curcumin | ||
| PubChem CID | 969516 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 368.4g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
1,6-Heptadiene-3,5-dione, 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-, (E,E)-, Curcumin, Curcumin Phytosome, Diferuloylmethane, Mervia, Phytosome, Curcumin, Turmeric Yellow, Yellow, Turmeric |
||
| Formula | C₂₁H₂₀O₆ | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C=CC(=O)CC(=O)C=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)OC)O | ||
| InChI | 1S/C21H20O6/c1-26-20-11-14(5-9-18(20)24)3-7-16(22)13-17(23)8-4-15-6-10-19(25)21(12-15)27-2/h3-12,24-25H,13H2,1-2H3/b7-3+,8-4+ | ||
| InChIKey | VFLDPWHFBUODDF-FCXRPNKRSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 8024-37-1 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL140 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:3962 | ||
| Herb ID | HBIN021985 | ||
| Drug Bank ID | DB11672 | ||
| Toxicity | Organism | Test Type | Route(Dose) |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal(165 mg/kg) | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal(254 mg/kg) | |
| rat | LD50 | oral(322 mg/kg) | |
| Structure | 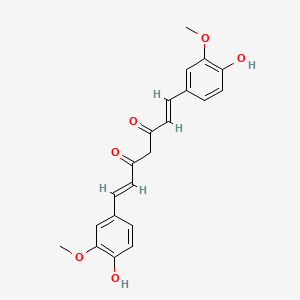
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | CaoGuo | ||
| Use Part | Fruit | ||
| Habitat | GuangXi, YunNan, GuiZhou | ||
| Flavor | Pungent | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Spleen, Stomach | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Zingiberales
-->Family: Zingiberaceae
-->Genus: Amomum
-->Species: Amomum tsao-ko
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | JiangHuang | ||
| Use Part | Tuberoid | ||
| Habitat | SiChuan, FuJian, GuangDong, ZheJiang, JiangXi | ||
| Flavor | Pungent, Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Spleen, Liver | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Zingiberales
-->Family: Zingiberaceae
-->Genus: Curcuma
-->Species: Curcuma longa
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | BaiChang | ||
| Habitat | China | ||
| Flavor | Pungent | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Acorales
-->Family: Acoraceae
-->Genus: Acorus
-->Species: Acorus calamus
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | GaoLiangJiang | ||
| Use Part | Rhizome | ||
| Habitat | HaiNan, GuangXi, YunNan, TaiWan, GuangDong | ||
| Flavor | Pungent | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Spleen, Stomach | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Zingiberales
-->Family: Zingiberaceae
-->Genus: Alpinia
-->Species: Alpinia officinarum
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | GuangXiEZhu | ||
| Use Part | Rhizome | ||
| Habitat | GuangXi, YunNan | ||
| Flavor | Pungent, Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Liver, Spleen | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Zingiberales
-->Family: Zingiberaceae
-->Genus: Curcuma
-->Species: Curcuma kwangsiensis
|
||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Celecoxib | |||
| Partner Name | Celecoxib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Proliferation | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | PTGS2 | hsa5743 |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| Result | Our findings show the prominent anti-proliferative effects of celecoxib and/or curcumin on MDA-MB-231 cells, providing a rationale for further detailed preclinical and potential clinical studies of this combination for breast cancer therapy. Further, these computed parameters suggested that curcumin possesses a high tendency to act as an adjuvant drug with celecoxib in the treatment of breast cancer. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Disulfiram | |||
| Partner Name | Disulfiram | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Oxidative stress | |||
| In Vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 |
| In Vivo Model | Tumor cells (2×10⁶ cells per 500 μL) were implanted subcutaneously into the left hind groin of mice. The compounds were dissolved in 5% DMSO and provided to the mice intraperitoneally once a day for 15 consecutive days. | |||
| Result | Combination Therapy of Curcumin and Disulfiram Synergistically Inhibits the Growth of B16-F10 Melanoma Cells by Inducing Oxidative Stress | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Apatinib | |||
| Partner Name | Apatinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | DIABLO | hsa56616 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BIRC5 | hsa332 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Result | Apa-Cur combination therapy exerts more profound anti-proliferation effects on breast cancer cell than Apatinib or Curcumin monotherapy. However, further studies are required to identify other possible signaling pathways and mechanisms involved in the anticancer effects of Apatinib, Curcumin, and Apa-Cur. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Docetaxel | |||
| Partner Name | Docetaxel | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B70] | Esophageal cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis and autophagy | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | PIK3CA | hsa5290 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MTOR | hsa2475 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP9 | hsa842 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| In Vitro Model | KYSE-150 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1348 |
| KYSE-510 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1354 | |
| Result | CUR combined with DTX induced apoptosis and autophagy of ESCC and probably worked through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. The combination of the autophagy inhibitor, CUR and DTX may become a new treatment strategy for esophageal cancer. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Arsenic oxide (As2O3) | |||
| Partner Name | Arsenic oxide (As2O3) | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | Prostate cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | VEGFA | hsa7422 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | VEGFC | hsa7424 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | KLK2 | hsa3817 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SNAIL | KEGG ID N.A. | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDH1 | hsa999 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| In Vitro Model | PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 |
| LNCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |
| Result | The antitumor effects of combination therapy with As2O3 and Curcumin have been displayed on prostate cancer cell lines (LNCaP and PC3), which probably originates from their potential to induce apoptosis and inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells simultaneously. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | GLS | hsa2744 |
| In Vitro Model | HT-29 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 |
| Result | These results indicate that curcumin could be clinically applied as an anti-chemoresistance approach against CRC by modulating miR-137-inhibited glutamine metabolism. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Olaparib | |||
| Partner Name | Olaparib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B66.Z] | Oral cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Chromatin remodeling | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | PARP1 | hsa142 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CHD1L | hsa9557 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | H3C1 | hsa8350 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | EP300 | hsa2033 | |
| In Vitro Model | H357 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2462 |
| Result | The present study reveals that Cur + Ola treatment increased oral cancer cell death not only through catalytic inhibition of PARP-1 but also predominantly through PARP-1 trapping and indirect inhibition of chromatin remodeling. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Anti-PD-1 antibody | |||
| Partner Name | Anti-PD-1 antibody | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C12] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Immune evasion | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | TGFB1 | hsa7040 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | EP300 | hsa2033 | |
| Down-regulation | Activity | SMAD2/3 | KEGG ID N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | Hep 3B2.1-7 | Childhood hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 |
| In Vivo Model | Hep3B cells in the logarithmic growth phase were suspended in 50% Matrigel (BD Biosciences) and adjusted to a density of 2×10⁶ cells/mL, and 0.2 mL of single-cell suspension was subcutaneously injected into the left axilla of each mouse. | |||
| Result | Synergistic efficacy of curcumin and anti-programmed cell death-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Vemurafenib | |||
| Partner Name | Vemurafenib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | EGFR | hsa1956 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | ROS1 | hsa6098 | |
| In Vitro Model | A375.S2 | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0136 |
| Result | Curcumin suppresses cell proliferation and triggers apoptosis in vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cells by downregulating the EGFR signaling pathway | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Carboplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Carboplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->DNA damage | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | ROS1 | hsa6098 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | RAD51 | hsa5888 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | H2AX | hsa3014 | |
| In Vitro Model | CAL-51 | Breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1110 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Result | Our data demonstrate that curcumin sensitizes TNBC to the anticancer effect of carboplatin by increasing ROS-induced DNA damage, thus providing an effective combination treatment strategy for TNBC. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Pyridoxine | |||
| Partner Name | Pyridoxine | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B91.Z] | Colorectal cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | PIK3CA | hsa5290 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | CTNNB1 | hsa1499 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | RELA | hsa5970 | |
| In Vivo Model | Male FVB mice (4 weeks old) were used in this study. | |||
| Result | C + B is superior to either agent alone in preventing obesity-promoted colorectal carcinogenesis. Augmented suppression of procancerous signaling pathways may be the means by which this augmentation occurs. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G2/M phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | SOX2 | hsa6657 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | NANOG | hsa79923 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | KLF4 | hsa9314 | |
| In Vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H2170 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1535 | |
| Result | Synergistic Roles of Curcumin in Sensitising the Cisplatin Effect on a Cancer Stem Cell-Like Population Derived from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Paclitaxel | |||
| Partner Name | Paclitaxel | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C73] | Ovarian cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | RELA | hsa5970 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | SNIP1 | hsa79753 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MCL1 | hsa4170 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | EGR1 | hsa1958 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | EP300 | hsa2033 | |
| Down-regulation | Activity | NFKB1 | hsa4790 | |
| In Vitro Model | SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| MDAH 2774 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0420 | |
| Result | Curcumin reduces paclitaxel resistance in ovarian carcinoma cells by upregulating SNIP1 and inhibiting NFκB activity | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Arsenic trioxide | |||
| Partner Name | Arsenic trioxide | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A60.Z] | Acute myeloid leukemia | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | JAK2 | hsa3717 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | STAT3 | hsa6774 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | PSMD9 | hsa5715 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| In Vitro Model | KG-1a | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1824 |
| In Vivo Model | All mice were inoculated with KG1-a cells via the tail vein after pretreatment of 48 h, approximately 1.0×10⁷ cells per mouse. | |||
| Result | Our results suggested that curcumin and As2O3 combination therapy exerts more significant anti-leukemia effects in the treatment of AML than curcumin or As2O3 monotherapy by up-regulating p53 pathway and down-regulating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand | |||
| Partner Name | TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C17] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Oxidative Stress-dependent apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | TNFRSF10B | hsa8795 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCR6 | hsa1235 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | DDX3X | hsa1654 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | GSK3B | hsa2932 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BIRC2 | hsa329 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP8 | hsa841 | |
| In Vitro Model | HuCCA-1 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_M255 |
| KKU-213A | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_M261 | |
| Result | The present study demonstrates the potential of using curcumin in combination with TRAIL to yield better TRAIL therapy outcomes in TRAIL-resistant CCA. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Binimetinib | |||
| Partner Name | Binimetinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Necroptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | MCL1 | hsa4170 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | RIPK3 | hsa11035 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | MLKL | hsa197259 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| In Vitro Model | G361 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C8ZL |
| SK-MEL-2 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0069 | |
| Result | Our data demonstrates that curcumin exerts significant synergistic anticancer effects on MM cells by inducing ROS and necroptosis when combined with binimetinib. Therefore, a strategy of adding curcumin to conventional anticancer agents holds promise for treating MM. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Docetaxel | |||
| Partner Name | Docetaxel | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C31.Z] | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Immunomodulatory | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | CD8A | hsa925 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CXCL1 | hsa2919 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | IFNG | hsa3458 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TNF | hsa7124 | |
| Result | Curcumin Enhances the Efficacy of Docetaxel by Promoting Anti-Tumor Immune Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Thalidomide | |||
| Partner Name | Thalidomide | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A60.Z] | Acute myeloid leukemia | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | BCL-xL | hsa598 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | STAT3 | hsa6774 | |
| In Vitro Model | KG-1a | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1824 |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 | |
| Result | Our findings suggested that down-regulation of STAT3 and BCL-XL mRNA expression in response to CUR and THAL treatment lead to inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptosis. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Fenretinide | |||
| Partner Name | Fenretinide | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Endoplasmic reticulum stress | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | HSPA5 | hsa3309 |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | PARP1 | hsa142 | |
| In Vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| In Vivo Model | LLC cells suspension (200 mL/mouse, 1×10⁷ cells/mL) was implanted carefully subcutaneously into the right side of the back of C57BL/6 mice | |||
| Result | Our findings suggest that the 2 small molecules, when used in combination, can potentially be effective therapeutic agents for treating NSCLC, at least in part, by regulating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone protein GRP78. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, HSV-TK/GCV | |||
| Partner Name | HSV-TK/GCV | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Gap junction activity | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | GJB1 | hsa2705 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | GJA1 | hsa2697 | |
| In Vitro Model | B16 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_F936 |
| In Vivo Model | A total of 2×10⁵ B16 cells in a final volume of 100L was injected into the right flanks of each C57BL/6J mouse | |||
| Result | Curcumin could enhance the killing effect and the bystander effect of HSV-TK/GCV in treating melanoma, which might be mediated by improved gap junction. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, 2-(2-Amino-3-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |||
| Partner Name | 2-(2-Amino-3-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B72.Z] | Gastric cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | PTEN | hsa5728 | |
| In Vitro Model | MGC-803 | Gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 |
| Result | Curcumin regulates the miR-21/PTEN/Akt pathway and acts in synergy with PD98059 to induce apoptosis of human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Nimustine | |||
| Partner Name | Nimustine | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A00] | Glioblastoma multiforme | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G2/M phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | COX2 | hsa4513 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | PIK3CA | hsa5290 | |
| In Vitro Model | U-118MG | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0633 |
| U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | |
| U-251MG | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0021 | |
| Result | Curcumin potentiates the potent antitumor activity of ACNU against glioblastoma by suppressing the PI3K/AKT and NF-kappaB/COX-2 signaling pathways | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Carfilzomib | |||
| Partner Name | Carfilzomib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A83.1] | Plasma cell myeloma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G0/G1 phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | CDKN1A | hsa1026 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | NFKBIA | hsa4792 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDH13 | hsa1012 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| In Vitro Model | U266B1 | Plasma cell myeloma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0566 |
| Result | Curcumin significantly ameliorates CFZ cytotoxic effect. Induction of p53/p21 axis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest were more pronounced for the CFZ-curcumin combination | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, ABT-888 | |||
| Partner Name | ABT-888 | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11:2B5Y] | Malignant mesenchymal neoplasm | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Homologous recombination | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | H2AX | hsa3014 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | RAD51 | hsa5888 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |
| U2OS | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| In Vivo Model | 2×10⁶ human MDA-MB-231 cells were prepared with 200 uL of PBS/matrigel gel (1:1 ratio) and injected subcutaneously into the flanks of athymic nude mice (two-site injections). | |||
| Result | Our study indicates that cotreatment of curcumin and PARP inhibitor might be useful for the combination chemotherapy for aggressive breast cancer treatment as a natural bioactive compound. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Doxorubicin | |||
| Partner Name | Doxorubicin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C12] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Angiogenesis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | VIM | hsa7431 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDH1 | hsa999 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| H22 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_H613 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c mice were subcutaneously implanted with H22 cells at a concentration of 1×10⁶ cells per mouse.Therapeutic drugs (DOX, 3 mg/kg; CUR, 0.75 mg/kg) were injected into the mice in the treated groups (saline, DC, DOX/Pep2, DOX/Pep1, DC/Pep2, DC/Pep1) via the tail vein every other day for 14 days starting on day 6. The tumor sizes and mouse body weights were measured every other day. | |||
| Result | Our findings provide a novel and simple approach to nhibit the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Dactolisib | |||
| Partner Name | Dactolisib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2D11.Y] | Neuroblastoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP7 | hsa840 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| In Vitro Model | SH-SY5Y | Neuroblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0019 |
| Result | Synergistic anti-proliferative and apoptotic effect of NVP-BEZ235 and curcumin on human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Melphalan | |||
| Partner Name | Melphalan | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP7 | hsa840 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP9 | hsa842 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDKN1A | hsa1026 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |
| MCF-10A | Healthy | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | |
| Result | Curcumin and melphalan cotreatment induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand | |||
| Partner Name | TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP9 | hsa842 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDKN1A | hsa1026 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK3 | hsa5595 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP2 | hsa4313 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP9 | hsa4318 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDH13 | hsa1012 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| Down-regulation | Activity | NFKB1 | hsa4790 | |
| In Vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Result | Combined treatment with curcumin and carboplatin inhibited tumor cell growth, migration, and invasion compared with either drug alone. The synergistic antitumor activity of curcumin combined with carboplatin is mediated by multiple mechanisms involving suppression of NF-kappaB via inhibition of the Akt/IKKalpha pathway and enhanced ERK1/2 activity | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, TRAIL/Apo2L | |||
| Partner Name | TRAIL/Apo2L | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C73] | Ovarian cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP8 | hsa841 |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP9 | hsa842 | |
| In Vitro Model | A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| SK-OV-3 | Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 | |
| ES-2 | Ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3509 | |
| Result | Combined curcumin and Apo2L/TRAIL treatment results in enhanced induction of apoptotic cell death. Because curcumin and Apo2L/TRAIL together can activate both the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways of apoptosis, they may circumvent chemoresistance to conventional chemotherapeutic agents. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Gemcitabine | |||
| Partner Name | Gemcitabine | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | MMP9 | hsa4318 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | VIM | hsa7431 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDH2 | hsa1000 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDH1 | hsa999 | |
| In Vitro Model | A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| In Vivo Model | A549/GEM resistant cells were collected and resuspended with PBS and injected into the tail veins of nude mice. For each mouse, 1×10⁶ cells in 150 μL of PBS were injected. | |||
| Result | Cur reversed GEM resistance and inhibited the EMT process in A549/GEM cells. GEM, combined with Cur, is safe and more effective in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Irinotecan | |||
| Partner Name | Irinotecan | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | CD24 | hsa100133941 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CD44 | hsa960 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | EPCAM | hsa4072 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | PROM1 | hsa8842 | |
| In Vitro Model | LoVo | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 |
| Result | The present data demonstrated that curcumin attenuated resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs through induction of apoptosis of CSCs among colon cancer cells. These findings may provide novel evidence for the therapeutic application of curcumin in CRC intervention. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Lenvatinib | |||
| Partner Name | Lenvatinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C12] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | EGFR | hsa1956 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MTOR | hsa2475 | |
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| SNU-449 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0454 | |
| PLC/PRF/5 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0485 | |
| SNU-398 | Adult hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0077 | |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0525 | |
| Result | We report that Curcumin reverses Lenvatinib resistance in HCC, and that their combination has clinical application potential for adjunctive treatment in HCC. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Quinacrine | |||
| Partner Name | Quinacrine | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Angiogenesis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | VEGFA | hsa7422 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | ABCG2 | hsa9429 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | PIK3CA | hsa5290 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | NOS3 | hsa4846 | |
| In Vitro Model | SP | Healthy | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C4PJ |
| In Vivo Model | The tumor tissue was cut into small pieces. Then, a deep incision was made in the anterior region of Balb/C mice using a scissor and then 5-6 chopped tumor tissue pieces were implanted in the anterior peritoneal wall within 3 h of collecting tumor tissues from the patient. | |||
| Result | Quinacrine and Curcumin in combination decreased the breast cancer angiogenesis by modulating ABCG2 via VEGF A | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Fluorouracil | |||
| Partner Name | Fluorouracil | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B91.Z] | Colorectal cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | STAT1 | hsa6772 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | L1CAM | hsa3897 | |
| In Vitro Model | SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 |
| In Vivo Model | SW620 cells (5×10⁶/0.1 ml Matrigel, Sigma-Aldrich) were injected subcutaneously into the lower right flank of female nude mice. | |||
| Result | We conclude that curcumin promotes chemosensitivity of CRC cells to 5-FU by downregulating L1 expression. Our findings provide experimental evidence for the synergism between curcumin and 5-FU, which can be utilized in clinical applications for reducing the toxicity and adverse effects of 5-FU. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Temozolomide | |||
| Partner Name | Temozolomide | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A00] | Glioblastoma multiforme | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | HSPB1 | hsa3315 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | HSPA4 | hsa3308 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | HSP90AA1 | hsa3320 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BDNF | hsa627 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TNF | hsa7124 | |
| In Vitro Model | U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 |
| Result | We showed for the first time that exosomes released from drug-treated U87 cells could be a new therapeutic approach in glioblastoma, and could reduce the side effects produced by drugs alone. This concept needs to be further examined in animal models before clinical trials could be considered. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Dasatinib | |||
| Partner Name | Dasatinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Cell invasion and colonosphere formation | |||
| In Vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| HT-29 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 | |
| Result | Our data suggest that the combination therapy of dasatinib and curcumin may be a therapeutic strategy for re-emergence of chemo-resistant colon cancer by targeting CSC sub-population. | |||
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Warfarin | |||
| Partner Name | Warfarin | |||
| Result | Increasing the risk of bleeding | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Probable interaction between an oral vitamin K antagonist and turmeric (Curcuma longa). Therapie. 2014;69(6):519-520. doi:10.2515/therapie/2014062 | Click |
| 2 | Quinacrine and Curcumin in combination decreased the breast cancer angiogenesis by modulating ABCG2 via VEGF A. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep;17(3):609-626. doi: 10.1007/s12079-022-00692-0. | Click |
| 3 | Low curcumin concentration enhances the anticancer effect of 5-fluorouracil against colorectal cancer. Phytomedicine. 2021 May;85:153547. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153547. | Click |
| 4 | Exosomes released from U87 glioma cells treated with curcumin and/or temozolomide produce apoptosis in naive U87 cells. Pathol Res Pract. 2023 May;245:154427. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154427. | Click |
| 5 | Combination of dasatinib and curcumin eliminates chemo-resistant colon cancer cells. J Mol Signal. 2011 Jul 20;6:7. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-6-7. | Click |
| 6 | Curcumin-Celecoxib: a synergistic and rationale combination chemotherapy for breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;25(4):1916-1927. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_25086. | Click |
| 7 | Combination Therapy of Curcumin and Disulfiram Synergistically Inhibits the Growth of B16-F10 Melanoma Cells by Inducing Oxidative Stress. Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 31;12(11):1600. doi: 10.3390/biom12111600. | Click |
| 8 | Anti-proliferation effects of Apatinib in combination with Curcumin in breast cancer cells. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2022 Sep 5;44(1):27-32. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2022-0036. | Click |
| 9 | Combination effect of curcumin with docetaxel on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to induce autophagy and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 2021 Jan 15;13(1):57-72. | Click |
| 10 | Human prostate cancer cell epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition as a novel target of arsenic trioxide and curcumin therapeutic approach. Tissue Cell. 2022 Jun;76:101805. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2022.101805. | Click |
| 11 | Curcumin Synergizes with Cisplatin to Inhibit Colon Cancer through Targeting the MicroRNA-137-Glutaminase Axis. Curr Med Sci. 2022 Feb;42(1):108-117. doi: 10.1007/s11596-021-2469-0. | Click |
| 12 | Olaparib enhances curcumin-mediated apoptosis in oral cancer cells by inducing PARP trapping through modulation of BER and chromatin assembly. DNA Repair (Amst). 2021 Sep;105:103157. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103157. | Click |
| 13 | Synergistic efficacy of curcumin and anti-programmed cell death-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci. 2021 Aug 15;279:119359. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119359. | Click |
| 14 | Curcumin suppresses cell proliferation and triggers apoptosis in vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cells by downregulating the EGFR signaling pathway. Environ Toxicol. 2022 Apr;37(4):868-879. doi: 10.1002/tox.23450. | Click |
| 15 | Curcumin sensitizes carboplatin treatment in triple negative breast cancer through reactive oxygen species induced DNA repair pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(4):3259-3270. doi:10.1007/s11033-022-07162-1. | Click |
| 16 | Combined Supplementation with Vitamin B-6 and Curcumin is Superior to Either Agent Alone in Suppressing Obesity-Promoted Colorectal Tumorigenesis in Mice. J Nutr. 2021 Dec 3;151(12):3678-3688. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxab320. | Click |
| 17 | Synergistic Roles of Curcumin in Sensitising the Cisplatin Effect on a Cancer Stem Cell-Like Population Derived from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules. 2021 Feb 18;26(4):1056. doi: 10.3390/molecules26041056. | Click |
| 18 | Curcumin reduces paclitaxel resistance in ovarian carcinoma cells by upregulating SNIP1 and inhibiting NFκB activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Jun;212:115581. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115581. | Click |
| 19 | Curcumin combined with arsenic trioxide in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia: network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jan;149(1):219-230. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04463-7. | Click |
| 20 | Potentiation of TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in TRAIL-Resistant Cholangiocarcinoma Cells by Curcumin through the Induction of DR5 Membrane Localization and Disruption of the Anti-Apoptotic Complex DR5/DDX3/GSK3β. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Feb 1;24(2):425-434. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.2.425. | Click |
| 21 | Curcumin Enhances the Anticancer Effects of Binimetinib on Melanoma Cells by Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Cell Apoptosis with Necroptosis. Ann Dermatol. 2023 Jun;35(3):217-228. doi: 10.5021/ad.22.200. | Click |
| 22 | Curcumin Enhances the Efficacy of Docetaxel by Promoting Anti-Tumor Immune Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Invest. 2023 May;41(5):524-533. doi: 10.1080/07357907.2023.2194420. | Click |
| 23 | Curcumin Combined with Thalidomide Reduces Expression of STAT3 and Bcl-xL, Leading to Apoptosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Jan 15;14:185-194. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S228610. | Click |
| 24 | Synergistic effect of fenretinide and curcumin for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2016 Oct 2;17(10):1022-1029. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1219810. | Click |
| 25 | Curcumin plays a synergistic role in combination with HSV-TK/GCV in inhibiting growth of murine B16 melanoma cells and melanoma xenografts. PeerJ. 2019 Sep 20;7:e7760. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7760. | Click |
| 26 | Curcumin regulates the miR-21/PTEN/Akt pathway and acts in synergy with PD98059 to induce apoptosis of human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells. J Int Med Res. 2019 Mar;47(3):1288-1297. doi: 10.1177/0300060518822213. | Click |
| 27 | Curcumin Potentiates the Potent Antitumor Activity of ACNU Against Glioblastoma by Suppressing the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB/COX-2 Signaling Pathways [Retraction]. Onco Targets Ther. 2022 Dec 2;15:1479-1480. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S399704. | Click |
| 28 | Curcumin ameliorates the in vitro efficacy of carfilzomib in human multiple myeloma U266 cells targeting p53 and NF-κB pathways. Toxicol In Vitro. 2018 Mar;47:186-194. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2017.12.001. | Click |
| 29 | Curcumin enhances poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor sensitivity to chemotherapy in breast cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 2015 Dec;26(12):1442-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.07.015. | Click |
| 30 | Morphologically transformable peptide nanocarriers coloaded with doxorubicin and curcumin inhibit the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mater Today Bio. 2023 Dec 12;24:100903. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100903. | Click |
| 31 | Synergistic anti-proliferative and apoptotic effect of NVP-BEZ235 and curcumin on human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Med Oncol. 2023 Dec 10;41(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02239-8. | Click |
| 32 | Curcumin and melphalan cotreatment induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 18;13(1):13446. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40535-5. | Click |
| 33 | Curcumin sensitizes human lung cancer cells to apoptosis and metastasis synergistically combined with carboplatin. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Nov;240(11):1416-25. doi: 10.1177/1535370215571881. | Click |
| 34 | Curcumin enhances Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis in chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2007 Apr;105(1):104-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.10.050. | Click |
| 35 | Curcumin enhances drug sensitivity of gemcitabine-resistant lung cancer cells and inhibits metastasis. Pharmazie. 2021 Nov 1;76(11):538-543. doi: 10.1691/ph.2021.0927. | Click |
| 36 | Curcumin attenuates resistance to irinotecan via induction of apoptosis of cancer stem cells in chemoresistant colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2018 Sep;53(3):1343-1353. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4461. | Click |
| 37 | Curcumin-Mediated Resistance to Lenvatinib via EGFR Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells. 2023;12(4):612. Published 2023 Feb 14. doi:10.3390/cells12040612. | Click |
