(+-)-sulforaphane, (R)-sulforaphane, (S)-sulforaphane, 1-isothiocyanato-4-methylsulphinylbutane, 4-methylsulfoxybutylisothiocyanate, sulforafan, sulforaphane, sulforaphane, (R)-, sulphoraphane



| Name | Sulforaphane | ||
| PubChem CID | 5350 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 177.3g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
(+-)-sulforaphane, (R)-sulforaphane, (S)-sulforaphane, 1-isothiocyanato-4-methylsulphinylbutane, 4-methylsulfoxybutylisothiocyanate, sulforafan, sulforaphane, sulforaphane, (R)-, sulphoraphane |
||
| Formula | C₆H₁₁NOS₂ | ||
| SMILES | CS(=O)CCCCN=C=S | ||
| InChI | 1S/C6H11NOS2/c1-10(8)5-3-2-4-7-6-9/h2-5H2,1H3 | ||
| InChIKey | SUVMJBTUFCVSAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 4478-93-7 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL48802 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:47807 | ||
| Herb ID | HBIN045133 | ||
| Drug Bank ID | DB12422 | ||
| Structure | 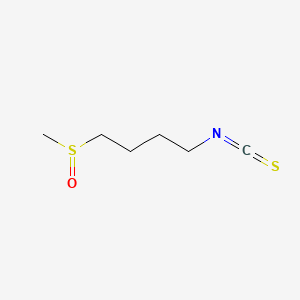
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | GanLan | ||
| Habitat | China | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Brassicales
-->Family: Brassicaceae
-->Genus: Brassica
-->Species: Brassica oleracea
|
||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | CDH1 | hsa999 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CLDN1 | hsa9076 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TJP1 | hsa7082 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDH2 | hsa1000 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | VIM | hsa7431 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CTNNB1 | hsa1499 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | ZEB1 | hsa6935 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SNAI2 | hsa6591 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SNAI1 | hsa6615 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP2 | hsa4313 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP9 | hsa4318 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SIRT1 | hsa23411 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SIRT2 | hsa22933 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SIRT3 | hsa23410 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SIRT5 | hsa23408 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SIRT7 | hsa51547 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Result | The results of the current study suggests that CIS when supplemented with SFN, inhibits metastasis and stemness potential of TNBC cells by down regulating SIRTs-mediated EMT cascade. Overall this study affirms that, this novel combination could be a promising strategy against SIRT-mediated TNBC metastasis and CIS-resistance. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, MiR-15b-5p | |||
| Partner Name | MiR-15b-5p | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | MIR15B | hsa406949 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP7 | hsa840 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAK1 | hsa578 | |
| In Vitro Model | HT-29 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 |
| Result | Our data demonstrate that this combined treatment leads to a very high proportion of apoptotic HT-29 cells (over 85%), a value higher than the sum of the values of apoptotic cells obtained after singularly administered regents (either SFN or R8-PNA-a15b). | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Metformin | |||
| Partner Name | Metformin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | ERBB2 | hsa2064 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SRC | hsa6714 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | WNT1 | hsa7471 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CTNNB1 | hsa1499 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CD44 | hsa960 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| In Vitro Model | BT-474 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 |
| Result | Our data indicate that SLFN and MTFN can reduce cancer cell viability via both collaborative and differential effects and suggest that MTFN increases SLFN effectiveness by targeting common molecules/pathways downstream of HER2 and key for CSC signaling. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Fluorouracil | |||
| Partner Name | Fluorouracil | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Autophagy | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | TYMS | hsa7298 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CASP8 | hsa841 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | MAP1LC3B | hsa81631 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCNB1 | hsa891 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| Result | Studies of the interaction mechanism have revealed that sulforaphane and 5-fluorouracil act synergistically in the MDA-MB-231 cells by inducing autophagic cell death and premature senescence. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, CB-5083 | |||
| Partner Name | CB-5083 | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | DDIT3 | hsa1649 |
| Down-regulation | Activity | NFKB1 | hsa4790 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | TWIST1 | hsa7291 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL-xL | hsa598 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SNAI1 | hsa6615 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | EGFR | hsa1956 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | NFKBIA | hsa4792 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | RELA | hsa5970 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| Result | The combination of Sulforaphane and CB-5083 may be a useful treatment strategy to combat CB-5083 resistance. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Lapatinib | |||
| Partner Name | Lapatinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B72.Z] | Gastric cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G0/G1 phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | ERBB2 | hsa2064 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC-7901 | Human papillomavirus-related cervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| Result | Therapeutic Mechanism of Lapatinib Combined with Sulforaphane on Gastric Cancer | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C28] | Malignant mesothelioma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G2/M phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | PARP1 | hsa142 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDKN1A | hsa1026 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCND1 | hsa595 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | CDK1 | hsa983 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MTOR | hsa2475 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | MAP1LC3B | hsa81631 | |
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H28 | Pleural sarcomatoid mesothelioma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1555 |
| Result | Pro-oxidant activity of sulforaphane and cisplatin potentiates apoptosis and simultaneously promotes autophagy in malignant mesothelioma cells | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Gefitinib | |||
| Partner Name | Gefitinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | CDH1 | hsa999 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CLDN1 | hsa9076 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDH2 | hsa1000 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | VIM | hsa7431 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | EGFR | hsa1956 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| In Vitro Model | PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 |
| Result | SFN overcame T790M-mediated gefitinib resistance in vitro through EMT. Thus, a combination of gefitinib and SFN may be a beneficial treatment strategy for lung cancer patients with acquired resistance due to T790M mutation. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Everolimus | |||
| Partner Name | Everolimus | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C94.Z] | Bladder cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | CDK1 | hsa983 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | CDK2 | hsa1017 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCNA2 | hsa890 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCNB1 | hsa891 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | RICTOR | hsa253260 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | RPTOR | hsa57521 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | H3C14 | hsa126961 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | HRH4 | hsa59340 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDKN2D | hsa1032 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | PSMD9 | hsa5715 | |
| In Vitro Model | RT-112 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 |
| UM-UC-3 | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1783 | |
| TCCSUP | Bladder carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1738 | |
| Result | The addition of SFN to the long-term everolimus application inhibits resistance development in bladder cancer cells in vitro. Therefore, sulforaphane may hold potential for treating bladder carcinoma in patients with resistance to an mTOR inhibitor. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, PP242 | |||
| Partner Name | PP242 | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B70] | Esophageal cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP9 | hsa842 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | RPS6KB1 | hsa6198 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | RICTOR | hsa253260 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1S1 | hsa84335 | |
| In Vitro Model | Eca-109 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6898 |
| EC9706 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_E307 | |
| Result | Our findings demonstrate that PP242 enhances the anti-tumor activity of SFN by blocking SFN-induced activation of Akt/mTOR pathway in ESCC, which provides a rationale for treating ESCC using SFN combined with Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Fluorouracil | |||
| Partner Name | Fluorouracil | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | CASP8 | hsa841 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| In Vitro Model | Caco-2 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 |
| LNCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |
| HT-29 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 | |
| PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | |
| Result | An increased cytostatic effect was observed in case of alyssin while for sulforaphane the synergistic interaction with 5-fluorouracil involved an intensification of apoptotic cell death. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, PR-104A | |||
| Partner Name | PR-104A | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | AKR1C3 | hsa8644 |
| In Vitro Model | HT-29 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 |
| SW620 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 | |
| Result | The enhanced response of PR-104A after preconditioning with SF was apparent only in cancer cells provided that AKR1C3 is expressed, while its expression in non-cancerous cells did not elicit such a response. Therefore, a subset of cancers may be susceptible to combined food-derived component and prodrug treatments with no harm to normal tissues. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Gemcitabine | |||
| Partner Name | Gemcitabine | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C12] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G2/M phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDKN1A | hsa1026 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | CHEK2 | hsa11200 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | CDC25C | hsa995 | |
| In Vitro Model | HuCC-T1 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0324 |
| HuH-28 | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2955 | |
| In Vivo Model | A million cells were suspended in 200 μL of medium containing Matrigel (Corning, Tewksbury, MA, USA; 1:1), and the same type of 1×10⁶ cells was inoculated subcutaneously into the bilateral flanks of each mouse. | |||
| Result | Sulforaphane Potentiates Gemcitabine-Mediated Anti-Cancer Effects against Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma by Inhibiting HDAC Activity | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand | |||
| Partner Name | TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | Prostate cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Angiogenesis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | BAK1 | hsa578 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL-xL | hsa598 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCNB1 | hsa891 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDK1 | hsa983 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDH13 | hsa1012 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| In Vitro Model | PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 |
| LNCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mice were inoculated with PC-3 cells (1×10⁶ per 100 AL medium) into the dorsolateral lobe of the prostatic capsule. | |||
| Result | The ability of sulforaphane to inhibit tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis and to enhance the therapeutic potential of TRAIL suggests that sulforaphane alone or in combination with TRAIL can be used for the management of prostate cancer. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Fernblock® XP | |||
| Partner Name | Fernblock® XP | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Cell metastasis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | IL1B | hsa3553 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP1 | hsa4312 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP3 | hsa4314 | |
| In Vitro Model | WM115 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0040 |
| WM266-4 | Melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2765 | |
| Result | SFN/FB was more efficient than SFN or FB alone in inhibiting MMP-1 and -3 production and IL-1β secretion in the presence of a pro-inflammatory stimulus such as TNF-α. The potential use of SFN/FB based supplements for the prevention of skin aging and as adjuvants in the treatment of advanced melanoma is suggested. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Clofarabine | |||
| Partner Name | Clofarabine | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | CDKN2A | hsa1029 |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Result | We showed that clofarabine in combination with sulforaphane, a phytochemical from cruciferous vegetables, significantly reactivates DNA methylation-silenced CDKN2A tumour suppressor and inhibits cancer cell growth at a non-invasive breast cancer stage. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C73] | Ovarian cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->DNA damage | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | MIR30A | hsa407029 |
| In Vitro Model | A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| IGROV-1 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1304 | |
| In Vivo Model | A2780/CP70 and IGROV1-R10 cells (4×10⁶) were injected into nude mice sub cutaneously. | |||
| Result | Our findings indicated that SFN could enhance cisplatin sensitivity of ovarian carcinoma cells through up-regulating miR-30a-3p to induce DNA damage and accumulation of intracellular cisplatin. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Acetazolamide | |||
| Partner Name | Acetazolamide | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | NANOGNB | hsa360030 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | POU5F1 | hsa5460 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SOX2 | hsa6657 | |
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H727 | Lung carcinoid tumor | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1584 |
| NCI-H720 | Lung carcinoid tumor | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1583 | |
| In Vivo Model | H727 and H720 parental and 3rd generation spheroid cells (3×10⁴) were injected into the subcutaneous inguinal fat pad of NOD/SCID mice. | |||
| Result | Human bronchial carcinoid tumor cells serially passaged as spheroids contain a higher fraction of TIC exhibiting a stemness phenotype. This TIC population can be effectively targeted by the combination of AZ + SFN. Our work portends clinical relevance and supports the therapeutic use of the novel AZ+ SFN combination that may target the TIC population of bronchial carcinoids. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Decitabine | |||
| Partner Name | Decitabine | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| In Vitro Model | B16-F10 | Mouse melanoma | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 |
| Result | These results indicate a potential combinatorial effect of a dietary antioxidant and an FDA-approved epigenetic drug in controlling melanoma cell growth. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Gefitinib | |||
| Partner Name | Gefitinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | SHH | hsa6469 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | GLI1 | hsa2735 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | GLI2 | hsa2736 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SMO | hsa6608 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | PROM1 | hsa8842 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CD44 | hsa960 | |
| In Vitro Model | PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 |
| Result | The results of the present study demonstrated that SFN inhibits the proliferation of gefitinib-tolerant lung cancer cells via modulation of the SHH signaling pathway. Therefore, combined SFN and gefitinib therapy may be an effective approach for the treatment of lung cancer. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Temozolomide | |||
| Partner Name | Temozolomide | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A00] | Glioblastoma multiforme | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | MGMT | hsa4255 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | RELA | hsa5970 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MKI67 | hsa4288 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP2 | hsa4313 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP9 | hsa4318 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| In Vitro Model | U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 |
| U-373MG ATCC | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2219 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse models were established with U373-R GBM cells inoculated subcutaneously into the right flanks of 4–6-week-old female mice. | |||
| Result | The present study suggests that the clinical efficacy of TMZ-based chemotherapy in TMZ-resistant GBM may be improved by combination with SFN. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Selenium | |||
| Partner Name | Selenium | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Protection oxidative damage | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | NFE2L2 | hsa4780 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TXNRD1 | hsa7296 | |
| In Vitro Model | CCD-841CoN | Healthy | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2871 |
| Result | Combined SFN and Se treatment synergistically upregulated TrxR-1, which plays a significant role in maintaining intracellular redox homeostasis and contributed to the SFN-induced protection against free radical-mediated oxidative damage in normal colonic cells. | |||
| Pair Name | Sulforaphane, Doxorubicin | |||
| Partner Name | Doxorubicin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Mitosis | |||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| MCF-10A | Healthy | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | |
| In Vivo Model | The 2×10⁵ 4T1 cells from in vitro culture in 0.05 mL PBS were injected into the mammary fat pad. | |||
| Result | Anticancer effect and safety of doxorubicin and nutraceutical sulforaphane liposomal formulation in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) animal model | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Synergy between sulforaphane and selenium in protection against oxidative damage in colonic CCD841 cells. Nutr Res. 2015 Jul;35(7):610-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2015.05.011. | Click |
| 2 | Anticancer effect and safety of doxorubicin and nutraceutical sulforaphane liposomal formulation in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) animal model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 May;161:114490. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114490. | Click |
| 3 | Sulforaphane-cisplatin combination inhibits the stemness and metastatic potential of TNBCs via down regulation of sirtuins-mediated EMT signaling axis. Phytomedicine. 2021 Apr;84:153492. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153492. | Click |
| 4 | High Levels of Apoptosis Are Induced in the Human Colon Cancer HT-29 Cell Line by Co-Administration of Sulforaphane and a Peptide Nucleic Acid Targeting miR-15b-5p. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020 Jun;30(3):164-174. doi: 10.1089/nat.2019.0825. | Click |
| 5 | Co-Treatment with Sulforaphane and Nano-Metformin Molecules Accelerates Apoptosis in HER2+ Breast Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Key Molecules. Nutr Cancer. 2020;72(5):835-848. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2019.1655073. | Click |
| 6 | Autophagic cell death and premature senescence: New mechanism of 5-fluorouracil and sulforaphane synergistic anticancer effect in MDA-MB-231 triple negative breast cancer cell line. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018 Jan;111:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.10.056. | Click |
| 7 | Sulforaphane is Synergistic with CB-5083 and Inhibits Colony Formation of CB-5083-Resistant HCT116 Cells. ChemMedChem. 2022 Jun 3;17(11):e202200030. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202200030. | Click |
| 8 | Therapeutic Mechanism of Lapatinib Combined with Sulforaphane on Gastric Cancer. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Sep 18;2021:9933274. doi: 10.1155/2021/9933274. | Click |
| 9 | Pro-oxidant activity of sulforaphane and cisplatin potentiates apoptosis and simultaneously promotes autophagy in malignant mesothelioma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017 Aug;16(2):2133-2141. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6789. | Click |
| 10 | Sulforaphane overcomes T790M-mediated gefitinib resistance in vitro through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;72(5). doi: 10.26402/jpp.2021.5.09. | Click |
| 11 | Chronic Sulforaphane Administration Inhibits Resistance to the mTOR-Inhibitor Everolimus in Bladder Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 4;21(11):4026. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114026. | Click |
| 12 | mTOR inhibitor PP242 increases antitumor activity of sulforaphane by blocking Akt/mTOR pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jan;49(1):451-461. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06895-9. | Click |
| 13 | In Vitro Evaluation of Sulforaphane and a Natural Analog as Potent Inducers of 5-Fluorouracil Anticancer Activity. Molecules. 2018 Nov 21;23(11):3040. doi: 10.3390/molecules23113040. | Click |
| 14 | Sulforaphane Preconditioning Sensitizes Human Colon Cancer Cells towards the Bioreductive Anticancer Prodrug PR-104A. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 7;11(3):e0150219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150219. | Click |
| 15 | Sulforaphane Potentiates Gemcitabine-Mediated Anti-Cancer Effects against Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma by Inhibiting HDAC Activity. Cells. 2023 Feb 22;12(5):687. doi: 10.3390/cells12050687. | Click |
| 16 | Sulforaphane enhances the therapeutic potential of TRAIL in prostate cancer orthotopic model through regulation of apoptosis, metastasis, and angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 1;14(21):6855-66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0903. | Click |
| 17 | The Combination of Sulforaphane and Fernblock® XP Improves Individual Beneficial Effects in Normal and Neoplastic Human Skin Cell Lines. Nutrients. 2020 May 30;12(6):1608. doi: 10.3390/nu12061608. | Click |
| 18 | Inhibition of breast cancer cell growth by the combination of clofarabine and sulforaphane involves epigenetically mediated CDKN2A upregulation. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2018;37(5):280-289. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2018.1453075. | Click |
| 19 | Sulforaphane enhances the cisplatin sensitivity through regulating DNA repair and accumulation of intracellular cisplatin in ovarian cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2020 Aug 15;393(2):112061. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112061. | Click |
| 20 | Human bronchial carcinoid tumor initiating cells are targeted by the combination of acetazolamide and sulforaphane. BMC Cancer. 2019 Aug 30;19(1):864. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6018-1. | Click |
| 21 | Effect of Sulforaphane and 5-Aza-2'-Deoxycytidine on Melanoma Cell Growth. Medicines (Basel). 2019 Jun 27;6(3):71. doi: 10.3390/medicines6030071. | Click |
| 22 | Sulforaphane reverses gefitinib tolerance in human lung cancer cells via modulation of sonic hedgehog signaling. Oncol Lett. 2018 Jan;15(1):109-114. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7293. | Click |
| 23 | Sulforaphane reverses chemo-resistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma cells by NF-κB-dependent pathway downregulating MGMT expression. Int J Oncol. 2016 Feb;48(2):559-68. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3271. | Click |
