(1,1'-biphenyl)-2,4'-diol, 3',5-di-2-propen-1-yl-, 3,5'-diallyl-4,2'-dihydroxybiphenyl, honokiol



| Name | Honokiol | ||
| PubChem CID | 72303 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 266.3g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
(1,1'-biphenyl)-2,4'-diol, 3',5-di-2-propen-1-yl-, 3,5'-diallyl-4,2'-dihydroxybiphenyl, honokiol |
||
| Formula | C₁₈H₁₈O₂ | ||
| SMILES | C=CCC1=CC(=C(C=C1)O)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)CC=C | ||
| InChI | 1S/C18H18O2/c1-3-5-13-7-9-18(20)16(11-13)14-8-10-17(19)15(12-14)6-4-2/h3-4,7-12,19-20H,1-2,5-6H2 | ||
| InChIKey | FVYXIJYOAGAUQK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 35354-74-6 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL16901 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:5759 | ||
| Herb ID | HBIN029531 | ||
| KEGG ID | C10630 | ||
| Structure | 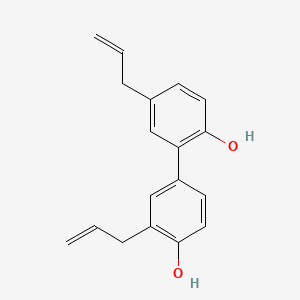
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | HouPu | ||
| Use Part | Bark | ||
| Habitat | SiChuan, HuBei | ||
| Flavor | Pungent; Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Spleen; Stomach; Lung; Large Intestine | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Magnoliales
-->Family: Magnoliaceae
-->Genus: Magnolia
-->Species: Magnolia officinalis
|
||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Osimertinib | |||
| Partner Name | Osimertinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | MCL1 | hsa4170 |
| In Vitro Model | PC-9 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 |
| PC-9-GR-high | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S706 | |
| HCC827 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| NCI-H1975/OSIR | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_WV99 | |
| In Vivo Model | The treatments included vehicle control, Osim (10 mg/kg/day, 5 days/week, og), HNK (50 mg/kg/day; ip), and their combination. | |||
| Result | Our findings warrant further study of HNK and its derivatives in overcoming Osim resistance in the clinic. | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Temozolomide | |||
| Partner Name | Temozolomide | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A00] | Glioblastoma multiforme | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis and autophagy | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 |
| In Vitro Model | U-87MG ATCC | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 |
| GL261 | Glioblastoma | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_Y003 | |
| Result | Taken together, this study demonstrated the improved effects of honokiol with TMZ on autophagy and subsequent apoptosis of drug-sensitive and -tolerant glioma cells. Thus, honokiol has the potential to be a drug candidate for treating human gliomas. | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Oxaliplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MAPK3 | hsa5595 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | RELA | hsa5970 | |
| In Vitro Model | HT-29 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 |
| Result | This combination allows a reduction in oxaliplatin dose, and thereby reduces its adverse effects. It may also enhance the chemotherapeutic effect of oxaliplatin for this disease. | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Chloroquine | |||
| Partner Name | Chloroquine | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | MAP1LC3A | hsa84557 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | SQSTM1 | hsa8878 | |
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 |
| A-549 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| Result | An enhanced antitumor effect was demonstrated following treatment with HNK combined with CQ by inhibiting autophagy and inducing apoptosis via a caspase-dependent and cathepsin D-involved manner. This combination may be a novel and useful antitumor approach for chemotherapy in NSCLC. | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Rapamycin | |||
| Partner Name | Rapamycin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | Renal cell carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->ROS generation | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | CD274 | hsa29126 |
| In Vitro Model | 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1051 |
| ACHN | Papillary renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1067 | |
| Result | Honokiol can effectively overcome the limitation of Rapamycin treatment alone; and the combination treatment can markedly restrict the growth of RCC, with particular importance to post-transplantation renal cancer. | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Rosiglitazone | |||
| Partner Name | Rosiglitazone | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C12] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G0/G1 phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | CCND1 | hsa595 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCNE1 | hsa898 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDKN1A | hsa1026 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | RB1 | hsa5925 | |
| In Vitro Model | Mahlavu | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0405 |
| SK-HEP-1 | Liver and intrahepatic bile duct epithelial neoplasm | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0525 | |
| Result | Honokiol combined with rosiglitazone showed more effective growth inhibition in hepatoma cells mediated through the regulation of G0/G1 phase-related proteins p21, cyclin D1, cyclin E1, and Rb and cell cycle progression | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Fluorouracil | |||
| Partner Name | Fluorouracil | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B62.0] | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | EGFR | hsa1956 | |
| In Vitro Model | HSC-3 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1288 |
| HSC-4 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1289 | |
| In Vivo Model | A total of 2×10⁶ HSC-3 cells were suspended in 100 uL serum-free DMEM and injected subcutaneously into the right flank of BALB/c nude mice to establish OSCC xenograft models | |||
| Result | These findings suggest that HNK and 5-FU exert a synergistic therapeutic effect on OSCC by inducing apoptosis. HNK might thus enhance the clinical therapeutic efficacy of 5-FU without increasing its toxicity. | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Cabozantinib | |||
| Partner Name | Cabozantinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | Renal cell carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Oxidative Stress | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL-xL | hsa598 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | RUBCN | hsa9711 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SQSTM1 | hsa8878 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | NFE2L2 | hsa4780 | |
| In Vitro Model | 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1051 |
| Caki-1 | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0234 | |
| Caki-2 | Papillary renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0235 | |
| ACHN | Papillary renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1067 | |
| In Vivo Model | 786-0 cells were subcutaneously injected into dorsal flank of 8-week-old male athymic nude mice and observed for the formation of tumors. The mice were then divided into four treatment groups (n = 5 mice per group): vehicle, XL-184, HNK, and XL-184 + HNK. Once the palpable tumor growth was observed, mice were treated with XL-184 (15 mg/kg), HNK (2 mg/kg) and XL-14 + HNK every alternate day for three weeks via intraperitoneal injection. | |||
| Result | Cabozantinib + Honokiol combination can significantly inhibit c-Met-induced and Nrf2-mediated anti-oxidant pathway in renal cancer cells to promote increased oxidative stress and tumor cell death. | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Paclitaxel | |||
| Partner Name | Paclitaxel | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G2/M phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | DDIT3 | hsa1649 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | ATF4 | hsa468 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | XBP1 | hsa7494 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | MAP1LC3A | hsa84557 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | PTEN | hsa5728 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDKN1A | hsa1026 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | PSMD9 | hsa5715 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK8 | hsa5599 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | NKRF | KEGG ID N.A. | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | MCL1 | hsa4170 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | PMAIP1 | hsa5366 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | EIF2S1 | hsa1965 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | HSPA5 | hsa3309 | |
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H1650 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1483 |
| NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| In Vivo Model | H1299 cells were washed three times with cold PBS and suspended at a final concentration of 1×10⁷/ml in PBS. Next 100 µl cell suspensions were subcutaneously injected into the right flanks of the mice. | |||
| Result | Synergistic killing effect of paclitaxel and honokiol in non-small cell lung cancer cells through paraptosis induction | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Metformin | |||
| Partner Name | Metformin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | RPS6KB1 | hsa6198 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | PARP1 | hsa142 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| SK-BR-3 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| Result | The combination of honokiol with metformin is considered an effective approach to induce death in hormone-resistant cells. Honokiol is of interest as a natural compound with antiproliferative activity against breast cancers, including resistant tumors. | |||
| Pair Name | Honokiol, Celecoxib | |||
| Partner Name | Celecoxib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | FOXM1 | hsa2305 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | FOXP3 | hsa50943 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | ITGAM | hsa3684 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MKI67 | hsa4288 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | NNT | hsa23530 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | PECAM1 | hsa5175 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | VEGFA | hsa7422 | |
| In Vitro Model | 4T1 | Malignant neoplasms of the mouse mammary gland | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0125 |
| Result | The combined treatment with PV-CXB and PV-HNK showed synergistic effect both in vitro and in vivo | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tuning mPEG-PLA/vitamin E-TPGS-based mixed micelles for combined celecoxib/honokiol therapy for breast cancer. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Apr 15;146:105277. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105277. | Click |
| 2 | Overcoming acquired resistance of EGFR-mutant NSCLC cells to the third generation EGFR inhibitor, osimertinib, with the natural product honokiol. Mol Oncol. 2020 Apr;14(4):882-895. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12645. | Click |
| 3 | Improved effects of honokiol on temozolomide-induced autophagy and apoptosis of drug-sensitive and -tolerant glioma cells. BMC Cancer. 2018 Apr 3;18(1):379. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4267-z. | Click |
| 4 | Honokiol augments the anti-cancer effects of oxaliplatin in colon cancer cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2013 Sep;45(9):773-9. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmt071. | Click |
| 5 | Honokiol exhibits enhanced antitumor effects with chloroquine by inducing cell death and inhibiting autophagy in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2015 Sep;34(3):1289-300. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4091. | Click |
| 6 | A Novel Combination Treatment with Honokiol and Rapamycin Effectively Restricts c-Met-Induced Growth of Renal Cancer Cells, and also Inhibits the Expression of Tumor Cell PD-L1 Involved in Immune Escape. Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 3;12(7):1782. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071782. | Click |
| 7 | Combined effect of honokiol and rosiglitazone on cell growth inhibition through enhanced G0/G1 phase arrest in hepatoma cells. J Chin Med Assoc. 2016 Aug;79(8):415-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2016.03.003. | Click |
| 8 | Synergistic effect of honokiol and 5-fluorouracil on apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Oral Pathol Med. 2017 Mar;46(3):201-207. doi: 10.1111/jop.12481. | Click |
| 9 | A novel combination therapy with Cabozantinib and Honokiol effectively inhibits c-Met-Nrf2-induced renal tumor growth through increased oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2023 Dec;68:102945. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102945. | Click |
| 10 | Synergistic killing effect of paclitaxel and honokiol in non-small cell lung cancer cells through paraptosis induction. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Feb;44(1):135-150. doi: 10.1007/s13402-020-00557-x. | Click |
| 11 | Honokiol inhibits the growth of hormone-resistant breast cancer cells: its promising effect in combination with metformin. Res Pharm Sci. 2023 Aug 20;18(5):580-591. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.383712. | Click |
