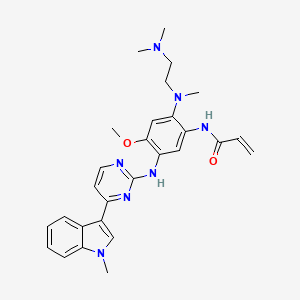
osimertinib, 1421373-65-0, AZD-9291, Mereletinib, AZD9291, AZD 9291, UNII-3C06JJ0Z2O, Osimertinib [USAN], osimertinibum, 3C06JJ0Z2O, AZD-9291 FREE BASE, N-(2-((2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl)(methyl)amino)-4-methoxy-5-((4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)acrylamide, N-(2-{[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl](Methyl)amino}-4-Methoxy-5-{[4-(1-Methyl-1h-Indol-3-Yl)pyrimidin-2-Yl]amino}phenyl)prop-2-Enamide, mereletinib (obsolete INN), N-[2-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl-methylamino]-4-methoxy-5-[[4-(1-methylindol-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]phenyl]prop-2-enamide, CHEBI:90943, 2-Propenamide, N-(2-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)methylamino)-4-methoxy-5-((4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)phenyl)-, AZD 9291(Osimertinib), N-(2-{[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl](methyl)amino}-4-methoxy-5-{[4-(1-methylindol-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}phenyl)prop-2-enamide, N-(2-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)methylamino)-4-methoxy-5-((4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)phenyl)-2-propenamide, N-[2-[[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]methylamino]-4-methoxy-5-[[4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-2-propenamide, Mereletinib [INN], C28H33N7O2, 2-Propenamide, N-[2-[[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]methylamino]-4-methoxy-5-[[4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-; N-[2-[[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]methylamino]-4-methoxy-5-[[4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-2-propenamide; AZD 9291; Osimertinib; Tagrisso, N-(2-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)(methyl)amino)-4-methoxy-5-((4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)prop-2-enamide, N-(2-{[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl](methyl)amino}-4-methoxy-5-{[4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}phenyl)acrylamide, OSIMERTINIB [MI], OSIMERTINIB [INN], Osimertinib (AZD9291), Osimertinib; AZD 9291, Osimertinib; AZD-9291, AZD-9291(Osimertinib)?, OSIMERTINIB [WHO-DD], GTPL7719, CHEMBL3353410, SCHEMBL14660911, AMY9161, EX-A314, L01XE35, MereletinibAZD-9291,Osimertinib, DUYJMQONPNNFPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N, DTXSID501025961, HMS3653E10, HMS3672M05, BCP08626, BDBM50029668, MFCD27988062, NSC779217, NSC781254, NSC800812, s7297, AKOS025290756, AZD-9291 , Mereletinib, CCG-264683, CS-2018, DB09330, NSC-779217, NSC-781254, NSC-800812, SB22952, NCGC00378622-03, NCGC00378622-04, NCGC00378622-10, AC-29019, AS-16943, HY-15772, 4714B, NS00073136, SW219863-1, EN300-7382438, A854509, Q21506464, N(2{[2(diMethylaMino)ethyl](Methyl)aMino}4Methoxy5{[4(1Methyl1Hindol3yl)pyriMidin2yl]aMino}phenyl)prop2enaMide;Osimertinib, N-(2-((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)(methyl)amino)-4-methoxy-5-(4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-ylamino)phenyl)acrylamide, N-(2-{2-Dimethylaminoethyl-methylamino}-4-methoxy-5-{[4-(1-methylindol-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino}phenyl)prop-2-enamide