lasidonin, oridonin, oridonin, (1alpha,5alpha,6alpha,7beta,8beta,9alpha,10beta,13beta,14S)-isomer, oridonin, (1alpha,6beta,7alpha,11alpha)-isomer, oridonin, (1alpha,6beta,7alpha,11beta)-isomer



| Name | Oridonin | ||
| PubChem CID | 5321010 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 364.4g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
lasidonin, oridonin, oridonin, (1alpha,5alpha,6alpha,7beta,8beta,9alpha,10beta,13beta,14S)-isomer, oridonin, (1alpha,6beta,7alpha,11alpha)-isomer, oridonin, (1alpha,6beta,7alpha,11beta)-isomer |
||
| Formula | C₂₀H₂₈O₆ | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC(C23C1C(C(C45C2CCC(C4O)C(=C)C5=O)(OC3)O)O)O)C | ||
| InChI | 1S/C20H28O6/c1-9-10-4-5-11-18-8-26-20(25,19(11,14(9)22)15(10)23)16(24)13(18)17(2,3)7-6-12(18)21/h10-13,15-16,21,23-25H,1,4-8H2,2-3H3/t10-,11-,12-,13+,15+,16-,18+,19-,20+/m0/s1 | ||
| InChIKey | SDHTXBWLVGWJFT-XKCURVIJSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 28957-04-2 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1164920 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:138236 | ||
| Herb ID | HBIN038254 | ||
| Toxicity | Organism | Test Type | Route(Dose) |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal(165 mg/kg) | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal(254 mg/kg) | |
| rat | LD50 | oral(322 mg/kg) | |
| Structure | 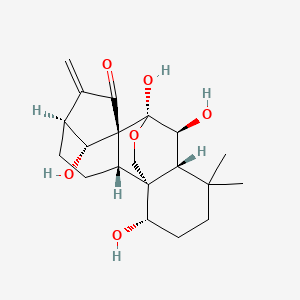
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | DongLingCao | ||
| Use Part | Whole Grass | ||
| Habitat | HeNan, HeBei, ShanXi, GanSu, SiChuan, GuiZhou, HuNan, HuBei, GuangXi, GuangDong, JiangXi, AnHui, ZheJiang | ||
| Flavor | Bitter, Sweet | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Lung, Stomach, Liver | ||
| Chineses Pinyin | LuShanXiangChaCai | ||
| Habitat | JiangSu, AnHui, ZheJiang, JiangXi, FuJian, TaiWan, HuBei, GuangDong, GuangXi, GuiZhou | ||
| Flavor | Pungent, Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Liver, Kidney | ||
| Chineses Pinyin | MaoGuoXiangChaCai | ||
| Chineses Pinyin | MaoYeXiangChaCai | ||
| Use Part | Leaf | ||
| Habitat | JiangSu, HeNan, SiChuan, GuiZhou, YunNan, XiZang, ChongQing, GanSu | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Lamiales
-->Family: Lamiaceae
-->Genus: Isodon
-->Species: Isodon japonicus
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | XianMaiXiangChaCai | ||
| Use Part | Whole Herb | ||
| Habitat | Shaanxi, HeNan, HuBei, JiangSu, ZheJiang, AnHui, JiangXi, GuangDong, GuangXi, GuiZhou, SiChuan | ||
| Flavor | Mildly pungent, Bitter | ||
| Chineses Pinyin | ZhouYeXiangChaCai | ||
| Use Part | Leaf | ||
| Habitat | XiZang, SiChuan, YunNan, Shaanxi, GanSu, QingHai, NingXia, XinJiang | ||
| Pair Name | Oridonin, Fluorouracil | |||
| Partner Name | Fluorouracil | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C90.Z] | Renal carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Necroptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Activity | MAPK8 | hsa5599 |
| Up-regulation | Activity | MAPK14 | hsa1432 | |
| Up-regulation | Activity | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| In Vitro Model | 786-O | Renal cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1051 |
| In Vivo Model | 786-O cells (1×10⁶) were subcutaneously injected into the right flank. | |||
| Result | Oridonin enhances the cytotoxicity of 5-FU in renal cancer cells partially through inducing necroptosis, providing evidence of using necroptosis inducers in combination with chemotherapeutic agents for cancer treatment. | |||
| Pair Name | Oridonin, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B70] | Esophageal cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->DNA damage | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | GSH | KEGG ID N.A. |
| Up-regulation | Expression | ROS1 | hsa6098 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | RAD51 | hsa5888 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | H2AX | hsa3014 | |
| In Vitro Model | KYSE-30 | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1351 |
| Result | These results suggest that ORI can synergistically enhance the effect of CIS, and GSH deficiency and p53 mutation, might be biomarkers for the combinational usage of ORI and CIS. | |||
| Pair Name | Oridonin, Cetuximab | |||
| Partner Name | Cetuximab | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C23.Z] | Laryngeal cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G2/M phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | FAS | hsa355 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | EGFR | hsa1956 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | ROS1 | hsa6098 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | MAPK8 | hsa5599 | |
| In Vitro Model | HEp-2 | Human papillomavirus-related cervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1906 |
| Tu 212 | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4915 | |
| In Vivo Model | Logarithmically growing HEp-2 cells were harvested by trypsinization, and each mouse was given injections of 1×10⁶ cells subcutaneously into the right flank. | |||
| Result | Combined oridonin with cetuximab treatment shows synergistic anticancer effects on laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Involvement of inhibition of EGFR and activation of reactive oxygen species-mediated JNK pathway | |||
| Pair Name | Oridonin, Arsenic oxide (As2O3) | |||
| Partner Name | Arsenic oxide (As2O3) | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C12] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | XIAP | hsa331 | |
| Down-regulation | Activity | NFKB1 | hsa4790 | |
| In Vivo Model | The two drug combination enhanced tumor suppression activity in murine HCC model compared with single agent treatment in vivo. | |||
| Result | The combination treatment induced ROS-dependent decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) decrease, and relocation of Bax and cytochrome C. Besides, oridonin dramatically increased the intracellular Ca2+ overload triggered by As2O3. Furthermore, the co-treatment of oridonin and As2O3 induced ROS-mediated down-regulation of Akt and XIAP, and inhibition of NF-κB activation. The two drug combination enhanced tumor suppression activity in murine HCC model compared with single agent treatment in vivo. | |||
| Pair Name | Oridonin, Imatinib | |||
| Partner Name | Imatinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B33.3] | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | RAF1 | hsa5894 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | JTK8 | hsa4067 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MEK1 | hsa5604 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MTOR | hsa2475 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | STAT5B | hsa6777 | |
| In Vitro Model | SUP-B15 | Childhood B acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0103 |
| Result | Our data showed that oridonin remarkably suppressed activations of Akt/mTOR, Raf/MEK and STAT5 pathway in these primary specimens and oridonin with imatinib exerted synergetic suppressive effects on mTOR, STAT5 and LYN signaling in one imatinib resistant patient specimen. Additional evaluation of oridonin as a potential therapeutic agent for Ph+ ALL seems warranted. | |||
| Pair Name | Oridonin, Venetoclax | |||
| Partner Name | Venetoclax | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A60.Z] | Acute myeloid leukemia | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | PARP1 | hsa142 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | H2AX | hsa3014 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL-xL | hsa598 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDKN1A | hsa1026 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | CDK2 | hsa1017 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MYC | hsa4609 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCND1 | hsa595 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | GSK3B | hsa2932 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MDM2 | hsa4193 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | TP53 | hsa7157 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BAD | hsa572 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BIM | hsa10018 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MCL1 | hsa4170 | |
| In Vitro Model | MOLM-13 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2119 |
| OCI-AML-3 | Adult acute myeloid leukemia | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1844 | |
| U-937 | Adult acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0007 | |
| THP-1 | Childhood acute monocytic leukemia | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0006 | |
| In Vivo Model | 5×10⁶ OCI-AML3 cells stably expressing luciferase were injected into the tail vein of NTG mice, and in vivo imaging was performed on the fourth day to confirm successful establishment of the AML xenografts. | |||
| Result | Oridonin and venetoclax synergistically promote AML cell apoptosis by inhibiting AKT signaling. | |||
| Pair Name | Oridonin, Doxorubicin | |||
| Partner Name | Doxorubicin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B51] | Osteosarcoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->ROS generation | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | ROS1 | hsa6098 |
| In Vitro Model | SaOS-2 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0548 |
| Result | The combined use of oridonin and doxorubicin could help to reduce the clinical dosage of doxorubicin and its dangerous side effects. | |||
| Pair Name | Oridonin, Doxorubicin | |||
| Partner Name | Doxorubicin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Angiogenesis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | KDR | hsa3791 |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| In Vivo Model | A breast tumor xenograft model was established via subcutaneous flank inoculation of BALB/c female nude mice with 1×10⁶ MDA-MB-231 cells in 100 μl PBS containing 50% Matrigel per mouse. | |||
| Result | Our findings provide strong evidence that Ori may be highly promising in enhancing the efficacy of Dox and decreasing its adverse cardiotoxic effects, thus suggesting that Ori may serve as a potential adjunct therapy during Dox-based chemotherapy. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Oridonin enhances antitumor effects of doxorubicin in human osteosarcoma cellsOridonin enhances antitumor effects of doxorubicin in human osteosarcoma cells. Pharmacol Rep. 2022 Feb;74(1):248-256. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00324-1. | Click |
| 2 | Oridonin synergistically enhances the anti-tumor efficacy of doxorubicin against aggressive breast cancer via pro-apoptotic and anti-angiogenic effects. Pharmacol Res. 2019 Aug;146:104313. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104313. | Click |
| 3 | Oridonin enhances the cytotoxicity of 5-FU in renal carcinoma cells by inducting necroptotic death. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:175-182. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.111. | Click |
| 4 | Selective synergistic anticancer effects of cisplatin and oridonin against human p53-mutant esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2022 Jan 1;33(1):e444-e452. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001237. | Click |
| 5 | Combined oridonin with cetuximab treatment shows synergistic anticancer effects on laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: involvement of inhibition of EGFR and activation of reactive oxygen species-mediated JNK pathway. Int J Oncol. 2016 Nov;49(5):2075-2087. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3696. | Click |
| 6 | Synergistic antitumor activity of oridonin and arsenic trioxide on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(1):139-147. doi:10.3892/ijo.2011.1210 | Click |
| 7 | Oridonin in combination with imatinib exerts synergetic anti-leukemia effect in Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells in vitro by inhibiting activation of LYN/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012 Nov;13(13):1244-54. doi: 10.4161/cbt.21460. | Click |
| 8 | Oridonin Synergistically Enhances the Pro-Apoptotic Effect of Venetoclax on Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells by Inhibiting AKT Signaling. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Sep 6;28(9):195. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2809195. | Click |
