


| Name | Bisdemethoxycucurmin | ||
| PubChem CID | 5315472 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 308.3g/mol | ||
| Formula | C₁₉H₁₆O₄ | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C=CC(=O)CC(=O)C=CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)O | ||
| InChI | 1S/C19H16O4/c20-16-7-1-14(2-8-16)5-11-18(22)13-19(23)12-6-15-3-9-17(21)10-4-15/h1-12,20-21H,13H2/b11-5+,12-6+ | ||
| InChIKey | PREBVFJICNPEKM-YDWXAUTNSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 33171-05-0 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL105350 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:71045 | ||
| Structure | 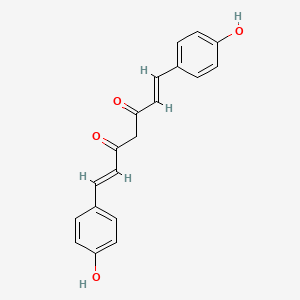
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | ShengJiang | ||
| Use Part | Fresh rhizome | ||
| Habitat | SiChuan, GuiZhou, HuBei, GuangDong, GuangXi | ||
| Flavor | Pungent | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Lung; Spleen; Stomach | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Zingiberales
-->Family: Zingiberaceae
-->Genus: Zingiber
-->Species: Zingiber officinale
|
||
| Pair Name | Bisdemethoxycucurmin, Icotinib | |||
| Partner Name | Icotinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis and autophagy | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | EGFR | hsa1956 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK8 | hsa5599 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | ERBB2 | hsa2064 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MET | hsa4233 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BIRC5 | hsa332 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | HDAC1 | hsa3065 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | HDAC2 | hsa3066 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | VDAC1 | hsa7416 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | VDAC2 | hsa7417 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | HK1 | hsa3098 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | GSK3B | hsa2932 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CYCS | hsa54205 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MAP1LC3A | hsa84557 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | MAP1LC3B | hsa81631 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SQSTM1 | hsa8878 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BECN1 | hsa8678 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP7 | hsa840 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | PARP1 | hsa142 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | ATM | hsa472 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | CHEK1 | hsa1111 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | TRIM28 | hsa10155 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | H2AX | hsa3014 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDH1 | hsa999 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | JUND | hsa3727 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | DNAJB4 | hsa11080 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP2 | hsa4313 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP9 | hsa4318 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | VEGFA | hsa7422 | |
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H460 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 |
| NCI-H1781 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1494 | |
| Result | Our data indicate that BMDC has the potential to improve the treatment of primary EGFR-TKI resistant NISCLC that cannot be controlled with single-target agent, such as icotinib. | |||
| Pair Name | Bisdemethoxycucurmin, Rapamycin | |||
| Partner Name | Rapamycin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Activity | MTOR | hsa2475 |
| Down-regulation | Activity | RPS6KB1 | hsa6198 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | TWIST1 | hsa7291 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP9 | hsa4318 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP9 | hsa842 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | GPR161 | hsa23432 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| BT-549 | Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1092 | |
| BT-20 | Invasive breast carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0178 | |
| Result | Bisdemethoxycurcumin Promotes Apoptosis and Inhibits the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through the Inhibition of the G-Protein-Coupled Receptor 161/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bisdemethoxycurcumin Enhances the Sensitivity of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Icotinib via Dual Induction of Autophagy and Apoptosis. Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Mar 5;16(9):1536-1550. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.40042. | Click |
| 2 | Bisdemethoxycurcumin Promotes Apoptosis and Inhibits the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through the Inhibition of the G-Protein-Coupled Receptor 161/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Dec 8;69(48):14557-14567. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c05585. | Click |
