All trans Lycopene, all-trans-lycopene, LYC O MATO, LYC-O-MATO, LYCOMATO, lycopene, lycopene, (13-cis)-isomer, Lycopene, (7-cis,7'-cis,9-cis,9'-cis)-isomer -, lycopene, (cis)-isomer, Pro Lycopene, Pro-Lycopene, prolycopene



| Name | Lycopene | ||
| PubChem CID | 446925 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 536.9g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
All trans Lycopene, all-trans-lycopene, LYC O MATO, LYC-O-MATO, LYCOMATO, lycopene, lycopene, (13-cis)-isomer, Lycopene, (7-cis,7'-cis,9-cis,9'-cis)-isomer -, lycopene, (cis)-isomer, Pro Lycopene, Pro-Lycopene, prolycopene |
||
| Formula | C₄₀H₅₆ | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCCC(=CC=CC(=CC=CC(=CC=CC=C(C)C=CC=C(C)C=CC=C(C)CCC=C(C)C)C)C)C)C | ||
| InChI | 1S/C40H56/c1-33(2)19-13-23-37(7)27-17-31-39(9)29-15-25-35(5)21-11-12-22-36(6)26-16-30-40(10)32-18-28-38(8)24-14-20-34(3)4/h11-12,15-22,25-32H,13-14,23-24H2,1-10H3/b12-11+,25-15+,26-16+,31-17+,32-18+,35-21+,36-22+,37-27+,38-28+,39-29+,40-30+ | ||
| InChIKey | OAIJSZIZWZSQBC-GYZMGTAESA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 502-65-8 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL501174 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:15948 | ||
| Herb ID | HBIN033972 | ||
| Drug Bank ID | DB11231 | ||
| KEGG ID | C05432 | ||
| Structure | 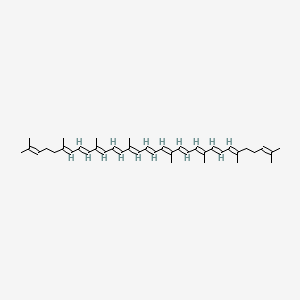
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | MeiGuiHua | ||
| Use Part | Bud | ||
| Habitat | BeiJing, TianJin, HeBei, ShanXi, NeiMengGu, Shaanxi, GanSu, QingHai, NingXia, XinJiang, SiChuan, GuiZhou, YunNan, XiZang, ChongQing, Japan , North Korea | ||
| Flavor | Sweet, Mildly bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Liver, Spleen | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Rosales
-->Family: Rosaceae
-->Genus: Rosa
-->Species: Rosa rugosa
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | NanHeShi | ||
| Use Part | Fruit | ||
| Habitat | JiangSu, HeNan, HuBei, ZheJiang | ||
| Flavor | Bitter, Pungent | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Spleen, Stomach | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Apiales
-->Family: Apiaceae
-->Genus: Daucus
-->Species: Daucus carota
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | ShenJinCao | ||
| Habitat | HuBei | ||
| Flavor | Mildly bitter, Pungent | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Liver, Spleen, Kidney | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Lycopodiales
-->Family: Lycopodiaceae
-->Genus: Lycopodium
-->Species: Lycopodium japonicum
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | ShiDi | ||
| Use Part | Calyx | ||
| Habitat | HeBei, HeNan, ShanDong | ||
| Flavor | Bitter, Astringent | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Stomach | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Ericales
-->Family: Ebenaceae
-->Genus: Diospyros
-->Species: Diospyros kaki
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | ShiYe | ||
| Use Part | Leaf | ||
| Habitat | HeBei, HeNan, ShanDong | ||
| Flavor | Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Lung | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Ericales
-->Family: Ebenaceae
-->Genus: Diospyros
-->Species: Diospyros kaki
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | HuaJuHong | ||
| Use Part | Pericarp | ||
| Habitat | ZheJiang, JiangXi, FuJian, TaiWan, HuBei, HuNan, GuangDong, GuangXi, SiChuan, GuiZhou, YunNan | ||
| Flavor | Pungent, Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Lung, Spleen | ||
| Chineses Pinyin | FanQie | ||
| Use Part | Fresh Fruit | ||
| Habitat | China | ||
| Flavor | Sour, Sweet | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Liver, Lung, Stomach | ||
| Chineses Pinyin | JinZhanJu | ||
| Use Part | Flower, Root | ||
| Habitat | FuJian, GuangDong, GuangXi, SiChuan, GuiZhou, YunNan | ||
| Flavor | Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Liver, Large intestine | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Asterales
-->Family: Asteraceae
-->Genus: Calendula
-->Species: Calendula officinalis
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | KuGua | ||
| Use Part | Fruit | ||
| Habitat | China | ||
| Flavor | Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Heart, Spleen, Lung | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Cucurbitales
-->Family: Cucurbitaceae
-->Genus: Momordica
-->Species: Momordica charantia
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | QianCengTa | ||
| Use Part | Whole Herb | ||
| Habitat | HeiLongJiang, JiLin, LiaoNing, SiChuan, GuiZhou, YunNan, XiZang, ChongQing | ||
| Flavor | Bitter, Mildly sweet | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Lung, Large intestine, Liver, Kidney | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Lycopodiales
-->Family: Lycopodiaceae
-->Genus: Huperzia
-->Species: Huperzia serrata
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | XiaoJieJinCao | ||
| Use Part | Whole Herb | ||
| Habitat | JiLin, Shaanxi, YunNan, SiChuan, XinJiang | ||
| Flavor | Mildly bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Heart | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Lycopodiales
-->Family: Lycopodiaceae
-->Genus: Huperzia
-->Species: Huperzia selago
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | YeHuLuoBo | ||
| Use Part | Root, Fruit | ||
| Habitat | SiChuan, GuiZhou, HuBei, JiangXi, AnHui, JiangSu | ||
| Flavor | Bitter, Pungent | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Apiales
-->Family: Apiaceae
-->Genus: Daucus
-->Species: Daucus carota
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | ZhongYaShaJi | ||
| Use Part | Fruit | ||
| Habitat | XinJiang | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Rosales
-->Family: Elaeagnaceae
-->Genus: Hippophae
-->Species: Hippophae rhamnoides
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | FanQie | ||
| Use Part | Fruit | ||
| Habitat | China | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Solanales
-->Family: Solanaceae
-->Genus: Lycopersicon
-->Species: Lycopersicon esculentum
|
||
| Pair Name | Lycopene, Anti-PD-1 antibody | |||
| Partner Name | Anti-PD-1 antibody | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Immunomodulatory | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | IFNG | hsa3458 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | JAK2 | hsa3717 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | STAT3 | hsa6774 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CXCL9 | KEGG ID N.A. | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CXCL10 | KEGG ID N.A. | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | DNMT3A | KEGG ID N.A. | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | IRF1 | hsa3659 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | IRF7 | KEGG ID N.A. | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | PD-L1 | KEGG ID N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | 3LL | Malignant tumors of the mouse pulmonary system | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_5653 |
| In Vivo Model | Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells (1×10⁶) were injected in the rear flak of C57BL/6 mice | |||
| Result | lycopene promoted anti-PD-1 therapeutic efficiency of lung cancer by promoting IFNγ-expressing CD8+ cells infiltrated in tumor tissues and increasing IFNγ expression in tumor cells. | |||
| Pair Name | Lycopene, Enzalutamide | |||
| Partner Name | Enzalutamide | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | Prostate cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | EZH2 | hsa2146 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | AR | hsa367 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP2 | hsa4313 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP9 | hsa4318 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | PCNA | hsa5111 | |
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP C4-2B | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4784 |
| 22Rv1 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1045 | |
| In Vivo Model | 22RV1 cells (2×10⁶) were injected into left tibia or the right flank of nude mice. | |||
| Result | These results suggest that the enhanced antitumor effects of enzalutamide by lycopene may be related to the reduction of AR protein levels through lycopene-mediated inhibition of AKT/EZH2 pathway, which may provide a new approach to improve the efficacy of enzalutamide in CRPC. | |||
| Pair Name | Lycopene, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C77.Z] | Cervical cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Oxidative Stress | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | NFKB1 | hsa4790 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDH13 | hsa1012 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | NFE2L2 | hsa4780 | |
| In Vitro Model | HeLa | Human papillomavirus-related cervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Result | Lycopene increases the sensitization of cervical cancer cells to cisplatin via inhibition of cell viability, up-regulation of Bax expression, and down-regulation of Bcl-2 expression. Furthermore, the anticancer effect of lycopene might be also associated with suppression of NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses, and modulation of Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress. The results of the present study suggest that lycopene and concurrent cisplatin chemotherapy might have a role in improving the treatment of cervical cancer. | |||
| Pair Name | Lycopene, Doxorubicin | |||
| Partner Name | Doxorubicin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP3 | hsa836 |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | PARP1 | hsa142 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| MDA-MB-468 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | |
| Result | Our results thus show the therapeutic benefit of red guava extracts as a potential cancer treatment for TNBC in combination with doxorubicin or targeted therapy. | |||
| Pair Name | Lycopene, Eicosapentaenoic acid | |||
| Partner Name | Eicosapentaenoic acid | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | FAS | hsa355 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MTOR | hsa2475 | |
| In Vitro Model | HT-29 | Colon adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 |
| Result | Our novel findings suggest that lycopene and EPA synergistically inhibited the growth of human colon cancer HT-29 cells even at low concentration. The inhibitory effects of lycopene and EPA on cell proliferation of human colon cancer HT-29 cells were, in part, associated with the down-regulation of the PI-3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. | |||
| Pair Name | Lycopene, T0901317 | |||
| Partner Name | T0901317 | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Cell proliferation | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | ABCA1 | hsa19 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | NR1H3 | hsa10062 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | PPARG | hsa5468 | |
| In Vitro Model | DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | |
| Result | These results demonstrate that lycopene can inhibit DU145 cell proliferation via PPARγ-LXRα-ABCA1 pathway and that lycopene and T0901317 exhibit synergistic effects. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lycopene improves the efficiency of anti-PD-1 therapy via activating IFN signaling of lung cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Mar 21;19:68. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0789-y. | Click |
| 2 | Lycopene enhances the sensitivity of castration-resistant prostate cancer to enzalutamide through the AKT/EZH2/ androgen receptor signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Jul 12;613:53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.04.126. | Click |
| 3 | Lycopene sensitizes the cervical cancer cells to cisplatin via targeting nuclear factor- kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 26;51(1):368-374. doi: 10.3906/sag-2005-413. | Click |
| 4 | Anti-cancer therapeutic benefit of red guava extracts as a potential therapy in combination with doxorubicin or targeted therapy for triple-negative breast cancer cells. Int J Med Sci. 2020 Apr 6;17(8):1015-1022. doi: 10.7150/ijms.40131. | Click |
| 5 | Concomitant supplementation of lycopene and eicosapentaenoic acid inhibits the proliferation of human colon cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 2009 Jun;20(6):426-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2008.05.001. | Click |
| 6 | Lycopene and the LXRα agonist T0901317 synergistically inhibit the proliferation of androgen-independent prostate cancer cells via the PPARγ-LXRα-ABCA1 pathway. J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Sep;23(9):1155-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.06.009. | Click |
