3 Pyridinecarboxamide, 3-Pyridinecarboxamide, B 3, Vitamin, B3, Vitamin, Enduramide, Jenapharm, Nicotinsäureamid, Niacinamide, Nicobion, Nicotinamide, Nicotinsäureamid Jenapharm, Papulex, Vitamin B 3, Vitamin B3, Vitamin PP



| Name | Niacinamide | ||
| PubChem CID | 936 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 122.12g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
3 Pyridinecarboxamide, 3-Pyridinecarboxamide, B 3, Vitamin, B3, Vitamin, Enduramide, Jenapharm, Nicotinsäureamid, Niacinamide, Nicobion, Nicotinamide, Nicotinsäureamid Jenapharm, Papulex, Vitamin B 3, Vitamin B3, Vitamin PP |
||
| Formula | C₆H₆N₂O | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CN=C1)C(=O)N | ||
| InChI | 1S/C6H6N2O/c7-6(9)5-2-1-3-8-4-5/h1-4H,(H2,7,9) | ||
| InChIKey | DFPAKSUCGFBDDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 98-92-0 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1140 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:17154 | ||
| Herb ID | HBIN036892 | ||
| Drug Bank ID | DB02701 | ||
| KEGG ID | C00153 | ||
| Toxicity | Organism | Test Type | Route(Dose) |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal(165 mg/kg) | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal(254 mg/kg) | |
| rat | LD50 | oral(322 mg/kg) | |
| Structure | 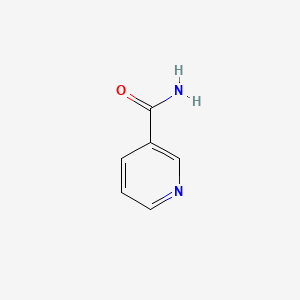
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | NiNanJie | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Brassicales
-->Family: Brassicaceae
-->Genus: Arabidopsis
-->Species: Arabidopsis thaliana
|
||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Gemcitabine | |||
| Partner Name | Gemcitabine | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C10.Z] | Pancreatic cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Immunomodulatory | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | HABP2 | hsa3026 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | PECAM1 | hsa5175 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CCL21 | hsa6366 | |
| In Vitro Model | Panc02 | Mouse pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_D627 |
| In Vivo Model | The spleen/pancreas was gently retracted and positioned to allow injection of Panc-02 tumor cells (1×10⁶/50 µL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)) directly into the pancreas, from the tail all the way to the head of the pancreas. | |||
| Result | This study highlights the potential of NAM+GEM as immunotherapy for advanced pancreatic cancer. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Tolbutamide | |||
| Partner Name | Tolbutamide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin human (zinc) | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin human (zinc) | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Metformin | |||
| Partner Name | Metformin | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin human (zinc extended) | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin human (zinc extended) | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Chlorpropamide | |||
| Partner Name | Chlorpropamide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Dapagliflozin | |||
| Partner Name | Dapagliflozin | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Dulaglutide | |||
| Partner Name | Dulaglutide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Empagliflozin | |||
| Partner Name | Empagliflozin | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Linagliptin | |||
| Partner Name | Linagliptin | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Pioglitazone | |||
| Partner Name | Pioglitazone | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Semaglutide | |||
| Partner Name | Semaglutide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin aspart (aspart) | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin aspart (aspart) | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin degludec | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin degludec | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin detemir | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin detemir | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin glargine | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin glargine | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin glulisine | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin glulisine | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin human (isophane) | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin human (isophane) | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin human (regular) | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin human (regular) | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Liraglutide | |||
| Partner Name | Liraglutide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Alogliptin | |||
| Partner Name | Alogliptin | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Glyburide | |||
| Partner Name | Glyburide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Canagliflozin | |||
| Partner Name | Canagliflozin | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Insulin lispro | |||
| Partner Name | Insulin lispro | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Lixisenatide | |||
| Partner Name | Lixisenatide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Miglitol | |||
| Partner Name | Miglitol | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Nateglinide | |||
| Partner Name | Nateglinide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Pramlintide | |||
| Partner Name | Pramlintide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Repaglinide | |||
| Partner Name | Repaglinide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Rosiglitazone | |||
| Partner Name | Rosiglitazone | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Saxagliptin | |||
| Partner Name | Saxagliptin | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Sitagliptin | |||
| Partner Name | Sitagliptin | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Tolazamide | |||
| Partner Name | Tolazamide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Ertugliflozin | |||
| Partner Name | Ertugliflozin | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Exenatide | |||
| Partner Name | Exenatide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Glimepiride | |||
| Partner Name | Glimepiride | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Glucobay | |||
| Partner Name | Glucobay | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Glipizide | |||
| Partner Name | Glipizide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| Pair Name | Niacinamide, Albiglutide | |||
| Partner Name | Albiglutide | |||
| Result | The efficacy of insulin and other antidiabetic agents may be diminished by certain drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, diuretics, estrogens, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, human growth hormone, phenothiazines, progestins, protease inhibitors, sympathomimetic amines, thyroid hormones, L-asparaginase, alpelisib, copanlisib, danazol, diazoxide, isoniazid, megestrol, omacetaxine, phenytoin, tagraxofusp, temsirolimus, as well as pharmacologic dosages of nicotinic acid and adrenocorticotropic agents. These drugs may interfere with blood glucose control because they can cause hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, new-onset diabetes mellitus, and/or exacerbation of preexisting diabetes. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 2 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 3 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 4 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 5 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 6 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 7 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 8 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 9 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 10 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 11 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 12 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 13 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 14 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 15 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 16 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 17 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 18 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 19 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 20 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 21 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 22 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 23 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 24 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 25 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 26 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 27 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 28 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 29 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 30 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 31 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 32 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 33 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 34 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 35 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 36 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 37 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 38 | DDInter: an online drug-drug interaction database towards improving clinical decision-making and patient safety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(D1):D1200-D1207. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab880 | Click |
| 39 | Nicotinamide combined with gemcitabine is an immunomodulatory therapy that restrains pancreatic cancer in mice. J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Nov;8(2):e001250. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001250. | Click |
