Berberine, Umbellatine



| Name | Berberine | ||
| PubChem CID | 2353 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 336.4g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
Berberine, Umbellatine |
||
| Formula | C₂₀H₁₈NO₄+ | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C2=C[N+]3=C(C=C2C=C1)C4=CC5=C(C=C4CC3)OCO5)OC | ||
| InChI | 1S/C20H18NO4/c1-22-17-4-3-12-7-16-14-9-19-18(24-11-25-19)8-13(14)5-6-21(16)10-15(12)20(17)23-2/h3-4,7-10H,5-6,11H2,1-2H3/q+1 | ||
| InChIKey | YBHILYKTIRIUTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 2086-83-1 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL295124 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:16118 | ||
| Herb ID | HBIN017893 | ||
| Drug Bank ID | DB04115 | ||
| KEGG ID | C00757 | ||
| Toxicity | Organism | Test Type | Route(Dose) |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal(165 mg/kg) | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal(254 mg/kg) | |
| rat | LD50 | oral(322 mg/kg) | |
| Structure | 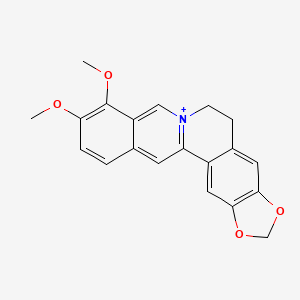
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | BaiHe | ||
| Use Part | Bulb | ||
| Habitat | China | ||
| Flavor | Sweet | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Heart, Lung | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Liliales
-->Family: Liliaceae
-->Genus: Lilium
-->Species: Lilium longiflorum
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | HuangLian | ||
| Use Part | Rhizome | ||
| Habitat | SiChuan, YunNan, HuBei | ||
| Flavor | Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Heart; Spleen; Stomach; Liver; Gallbladder; Large Intestine | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Ranunculales
-->Family: Ranunculaceae
-->Genus: Coptis
-->Species: Coptis chinensis
|
||
| Pair Name | Berberine, Erlotinib | |||
| Partner Name | Erlotinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | EGFR | hsa1956 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCND1 | hsa595 | |
| In Vitro Model | A-431 | Skin squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0037 |
| NCI-H1666 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1485 | |
| NCI-H441 | Lung papillary adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1561 | |
| NCI-H1781 | Minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1494 | |
| In Vivo Model | A431 cells (5×10⁶) were suspended in 200 µL of normal saline and subcutaneously implanted into 6-7-week-old male athymic nude mice. | |||
| Result | Our data supported use of BBR in combination with erlotinib as a novel strategy for treatment of patients with EGFR positive tumors. | |||
| Pair Name | Berberine, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B51] | Osteosarcoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G0/G1 phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | MMP2 | hsa4313 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MMP9 | hsa4318 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCND1 | hsa595 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDK4 | hsa1019 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK14 | hsa1432 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK8 | hsa5599 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| In Vitro Model | MG-63 | Osteosarcoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0426 |
| Result | Berberine and Cisplatin Exhibit Synergistic Anticancer Effects on Osteosarcoma MG-63 Cells by Inhibiting the MAPK Pathway | |||
| Pair Name | Berberine, Niraparib | |||
| Partner Name | Niraparib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C73] | Ovarian cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->DNA damage | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | RAD51 | hsa5888 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | NR1H4 | KEGG ID N.A. | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | H2AX | hsa3014 | |
| In Vitro Model | A2780 | Ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| HO-8910 | Human papillomavirus-related cervical adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6868 | |
| In Vivo Model | The animals were subcutaneously inoculated with 1 × 106 A2780 cells (suspended in 100 μl PBS) and six days later the tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into four groups and were then treated daily by oral gavage with vehicle (sodium carboxymethycellulose, SCMC), berberine (200 mg/kg bodyweight), niraparib (40 mg/kg bodyweight) and berberine (200 mg/kg) in combination with niraparib (40 mg/kg), respectively, for 15 days. | |||
| Result | The results indicate that by inducing oxidative DNA damage and downregulating HRR in cancer cells berberine is able to further sensitize cancer cells to PARP inhibition. These results demonstrate a potential therapeutic value of combined application of berberine and PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer treatment. | |||
| Pair Name | Berberine, Letrozole | |||
| Partner Name | Letrozole | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | ROS1 | hsa6098 |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| Result | Our results suggest that concomitant treatment of LTZ-BBR increases the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents with low BBR concentrations, especially in chemo-resistant malignancies. | |||
| Pair Name | Berberine, Lapatinib | |||
| Partner Name | Lapatinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->ROS generation | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | ROS1 | hsa6098 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MYC | hsa4609 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | NFE2L2 | hsa4780 | |
| In Vitro Model | BT-474LabR | Lapatinib-resistant breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| AU-565LapR | Lapatinib-resistant breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Result | Berberine can upset the ROS balance by downregulating c-Myc to reverse the Lapatinib resistance. Our finding provides a novel strategy of using berberine to overcome Lapatinib resistance. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Antitumor effects of erlotinib in combination with berberine in A431 cells. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 May 11;24(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40360-023-00661-2. | Click |
| 2 | Berberine and Cisplatin Exhibit Synergistic Anticancer Effects on Osteosarcoma MG-63 Cells by Inhibiting the MAPK Pathway. Molecules. 2021 Mar 17;26(6):1666. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061666. | Click |
| 3 | Berberine induces oxidative DNA damage and impairs homologous recombination repair in ovarian cancer cells to confer increased sensitivity to PARP inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(10):e3070. Published 2017 Oct 5. doi:10.1038/cddis.2017.471 | Click |
| 4 | Synergistic Combination of Letrozole and Berberine in Ascorbic Acid-Stabilized AuNPs: A Promising Solution for Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 3;16(8):1099. doi: 10.3390/ph16081099. | Click |
| 5 | Berberine reverses Lapatinib resistance of HER2-positive breast cancer cells by increasing the level of ROS. Cancer Biol Ther. 2016;17(9):925-934. doi:10.1080/15384047.2016.1210728 | Click |
