2-methyl-5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, 5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone, plumbagin



| Name | Plumbagin | ||
| PubChem CID | 10205 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 188.18g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
2-methyl-5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, 5-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone, plumbagin |
||
| Formula | C₁₁H₈O₃ | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=O)C2=C(C1=O)C=CC=C2O | ||
| InChI | 1S/C11H8O3/c1-6-5-9(13)10-7(11(6)14)3-2-4-8(10)12/h2-5,12H,1H3 | ||
| InChIKey | VCMMXZQDRFWYSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 481-42-5 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL295316 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:8273 | ||
| Herb ID | HBIN040266 | ||
| Drug Bank ID | DB17048 | ||
| KEGG ID | C10387 | ||
| Toxicity | Organism | Test Type | Route(Dose) |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal(165 mg/kg) | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal(254 mg/kg) | |
| rat | LD50 | oral(322 mg/kg) | |
| Structure | 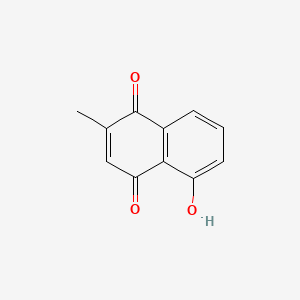
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | BaiHuaDan | ||
| Use Part | Whole Grass, Root | ||
| Habitat | FuJian, TaiWan, GuangDong, GuangXi | ||
| Flavor | Pungent, Bitter | ||
| Chineses Pinyin | ZiJinLian | ||
| Use Part | Root | ||
| Habitat | GanSu, HeBei, ShanXi, JiangSu, ZheJiang, HeNan | ||
| Flavor | Pungent, Sweet | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Liver | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Caryophyllales
-->Family: Plumbaginaceae
-->Genus: Ceratostigma
-->Species: Ceratostigma willmottianum
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | MaoGaoCai | ||
| Use Part | Whole Herb | ||
| Habitat | SiChuan, GuiZhou, YunNan, XiZang, JiangSu, ZheJiang, AnHui, FuJian, JiangXi, HuBei, HuNan, GuangDong, GuangXi, HaiNan, TaiWan | ||
| Flavor | Sweet, Pungent | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Spleen | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Caryophyllales
-->Family: Droseraceae
-->Genus: Drosera
-->Species: Drosera peltata
|
||
| Pair Name | Plumbagin, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B62.0] | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->ROS accumulation | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | ROS1 | hsa6098 |
| Up-regulation | Activity | MAPK8 | hsa5599 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MTOR | hsa2475 | |
| In Vitro Model | CAL-27 | Tongue adenosquamous carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1107 |
| In Vivo Model | Each mouse was injected with 0.15 mL of cell suspension containing 1×10⁶ CAL27/CDDP cells into the right flanks. | |||
| Result | PLB combined with cisplatin is a potential therapeutic strategy against therapy TSCC cisplatin resistance. | |||
| Pair Name | Plumbagin, Zoledronic acid | |||
| Partner Name | Zoledronic acid | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C60] | Breast cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 |
| Up-regulation | Expression | NOTCH1 | hsa4851 | |
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 | Breast adenocarcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| Result | Combination of ZA and PL synergistically suppresses human breast cancer MDA-MB-231SArfp cells in vitro. PL can inhibit ZA-induced activation of the Notch-1 signaling pathway and subsequently reduce the expression of Bcl-2, thus potentiating cancer cell apoptosis. | |||
| Pair Name | Plumbagin, Celecoxib | |||
| Partner Name | Celecoxib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | COX2 | hsa4513 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | STAT3 | hsa6774 | |
| In Vitro Model | UACC-903 | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4052 |
| Mel JuSo | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1403 | |
| A375-M | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B222 | |
| 1205Lu | Cutaneous melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5239 | |
| In Vivo Model | Subcutaneous injection of 1.0×10⁶ UACC 903 or 1205 Lu melanoma cells were injected above both the left and right rib cages of 4-5 week-old female Athymic-Foxn1nu nude mice | |||
| Result | Combination of Celecoxib and Plumbagin decreased melanoma cell proliferation and retarded vascular development of tumors mediated by inhibition of COX-2 and STAT3 leading to decreased levels of key cyclins key on which melanoma cell were dependent for survival. | |||
| Pair Name | Plumbagin, rsTRAIL | |||
| Partner Name | rsTRAIL | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B33.4] | Leukemia | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->ROS generation | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | TNFRSF10B | hsa8795 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CFLAR | hsa8837 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAX | hsa581 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BID | hsa637 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP8 | hsa841 | |
| In Vitro Model | Kasumi-1 | Childhood acute myeloid leukemia with maturation | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0589 |
| In Vivo Model | Kasumi-1 cells were injected s.c. into the flanks of the mice (2.5×10⁶ in 2 ml) and tumors were allowed to develop for 18–30 days until they reached 50–100 mm3, then treatment was initiated. | |||
| Result | Our results suggest that both plumbagin and rsTRAIL could be used as a single agent or synergistical agents to induce apoptosis of leukemic Kasumi‑1 cells in vitro and in vivo. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plumbagin Enhances the Anticancer Efficacy of Cisplatin by Increasing Intracellular ROS in Human Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Mar 25;2020:5649174. doi: 10.1155/2020/5649174. | Click |
| 2 | Synergistic suppression of human breast cancer cells by combination of plumbagin and zoledronic acid In vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Sep;36(9):1085-98. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.42. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Erratum in: Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Aug;40(8):1127-1128. | Click |
| 3 | Synergistic inhibitory effects of Celecoxib and Plumbagin on melanoma tumor growth. Cancer Lett. 2017 Jan 28;385:243-250. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.10.016. | Click |
| 4 | Plumbagin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis of human leukemic Kasumi‑1 cells through upregulation of TRAIL death receptor expression, activation of caspase-8 and inhibition of cFLIP. Oncol Rep. 2017;37(6):3423-3432. doi:10.3892/or.2017.5627 | Click |
