morusin



| Name | Morusin | ||
| PubChem CID | 5281671 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 420.5g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
morusin |
||
| Formula | C₂₅H₂₄O₆ | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCC1=C(OC2=C(C1=O)C(=CC3=C2C=CC(O3)(C)C)O)C4=C(C=C(C=C4)O)O)C | ||
| InChI | 1S/C25H24O6/c1-13(2)5-7-17-22(29)21-19(28)12-20-16(9-10-25(3,4)31-20)24(21)30-23(17)15-8-6-14(26)11-18(15)27/h5-6,8-12,26-28H,7H2,1-4H3 | ||
| InChIKey | XFFOMNJIDRDDLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 62596-29-6 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL464006 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:7005 | ||
| Herb ID | HBIN035791 | ||
| KEGG ID | C10106 | ||
| Structure | 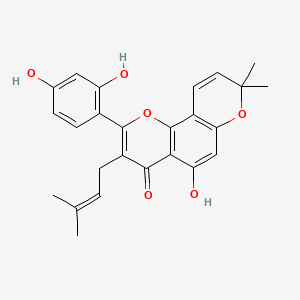
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | BaiJiangCao | ||
| Use Part | Whole Grass, Rhizome, Root | ||
| Habitat | SiChuan, JiangXi, FuJian | ||
| Flavor | Pungent, Bitter | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Stomach, Large intestine, Liver | ||
| Chineses Pinyin | DaFengZi | ||
| Use Part | Seed | ||
| Habitat | GuangDong, HaiNan, YunNan, GuangXi, TaiWan, FuJian | ||
| Flavor | Pungent | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Liver, Spleen, Kidney | ||
| Chineses Pinyin | GanCao | ||
| Use Part | Root, Rhizome | ||
| Habitat | HeiLongJiang, JiLin, LiaoNing, NeiMengGu, GanSu, XinJiang | ||
| Flavor | Sweet | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Heart, Lung, Spleen, Stomach | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Fabales
-->Family: Fabaceae
-->Genus: Glycyrrhiza
-->Species: Glycyrrhiza uralensis
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | SangBaiPi | ||
| Use Part | Root Bark | ||
| Habitat | China | ||
| Flavor | Sweet | ||
| Meridian Tropism | Lung | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Rosales
-->Family: Moraceae
-->Genus: Morus
-->Species: Morus alba
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | MengSang | ||
| Use Part | Root Cortex | ||
| Habitat | HeiLongJiang, JiLin, LiaoNing, NeiMengGu, XinJiang, QingHai, HeBei, ShanXi, HeNan, ShanDong, Shaanxi, AnHui, JiangSu, HuBei, SiChuan, GuiZhou, YunNan | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Rosales
-->Family: Moraceae
-->Genus: Morus
-->Species: Morus mongolica
|
||
| Chineses Pinyin | JiSang | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Magnoliopsida
-->Order: Rosales
-->Family: Moraceae
-->Genus: Morus
-->Species: Morus australis
|
||
| Pair Name | Morusin, MAPK pathway inhibitors | |||
| Partner Name | MAPK pathway inhibitors | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | STAT3 | hsa6774 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | PARP1 | hsa142 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCND1 | hsa595 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | SOX2 | hsa6657 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MYC | hsa4609 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BIRC5 | hsa332 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | PCNA | hsa5111 | |
| In Vitro Model | A-375 | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 |
| In Vivo Model | A375 and A375R cells (1×10⁵, in 100 μL of phosphate-buffered saline) were subcutaneously injected into the right hind legs of 4-week-old male BALB/c nude mice. | |||
| Result | Our results suggested that the combination of morusin and MAPK pathway inhibitors may be a more effective treatment strategy for BRAF-mutant melanoma than MAPK pathway inhibitors alone. | |||
| Pair Name | Morusin, TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand | |||
| Partner Name | TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2A00] | Glioblastoma multiforme | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | TNFRSF10B | hsa8795 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BIRC5 | hsa332 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | XIAP | hsa331 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | EGFR | hsa1956 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | STAT3 | hsa6774 | |
| In Vitro Model | U-251MG | Astrocytoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0021 |
| LN-18 | Glioblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0392 | |
| Result | These results suggest that morusin enhances TRAIL sensitivity in human glioblastoma cells through regulating expression of DR5 and EGFR. Therefore, the combination treatment of TRAIL and morusin may be a new therapeutic strategy for malignant glioma patients. | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Morusin Induces TRAIL Sensitization by Regulating EGFR and DR5 in Human Glioblastoma Cells. J Nat Prod. 2016 Feb 26;79(2):317-23. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00919. | Click |
| 2 | Morusin enhances the antitumor activity of MAPK pathway inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanoma by inhibiting the feedback activation of STAT3. Eur J Cancer. 2022 Apr;165:58-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2022.01.004. | Click |
