


| Pair Name | Xanthohumol, Praziquantel | ||
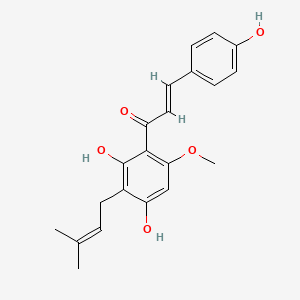
| Phytochemical Name | Xanthohumol (PubChem CID: 639665 ) | ||
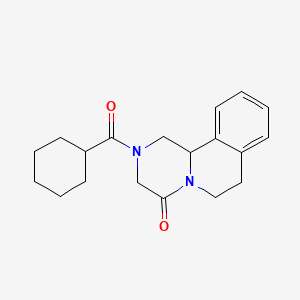
| Anticancer drug Name | Praziquantel (PubChem CID: 4891 ) | ||
| Structure of Phytochemical |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Structure of Anticancer Drug |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Pair Name | Xanthohumol, Praziquantel | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C12] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Oxidative Stress | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | CD44 | hsa960 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK14 | hsa1432 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | TFRC | hsa7037 | |
| In Vivo Model | Six- to eight-week-old male Syrian golden hamsters were randomly divided into four groups as followings: group I, Ov infection and NDMA administration (ON); group II, Ov infection and NDMA administration and PZ treatment (ONP); groups III and IV were similar to group I and II, they received 20 μM XN (171 mg/B.W./day) designated as XON and XONP groups, respectively. | |||
| Result | XN administered in combination with PZ could efficiently prevent CCA development and hence provide potential chemopreventive benefits in Ov-induced cholangiocarcinogenesis | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Antifibrotic effect of xanthohumol in combination with praziquantel is associated with altered redox status and reduced iron accumulation during liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinogenesis. PeerJ. 2018 Jan 22;6:e4281. doi: 10.7717/peerj.4281. | Click |
